Characterization of Human Adrenal Steroidogenesis During Fetal Development
- PMID: 30590593
- PMCID: PMC6456011
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2018-01759
Characterization of Human Adrenal Steroidogenesis During Fetal Development
Abstract
Context: The endocrine function of human fetal adrenals (HFAs) is activated already during first trimester, but adrenal steroidogenesis during fetal life is not well characterized.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate HFA steroidogenesis by analyzing adrenal glands from first and second trimesters.
Design and setting: Male and female HFA from gestational weeks (GWs) 8 to 19 were examined, including a total of 101 samples from 83 fetuses.
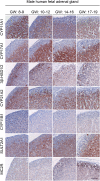
Main outcome measure(s): Expression level of steroidogenic genes and protein expression/localization were determined by quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry, respectively, and intra-adrenal steroid levels were quantified by LC-MS/MS.
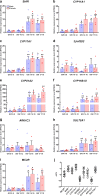
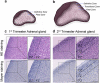
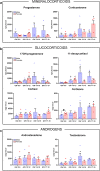
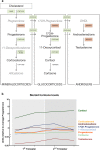
Results: Transcriptional levels of StAR, CYP11A1, CYP17A1, CYP21A2, CYP11B1/2, and SULT2A1 were significantly higher in second trimester compared to first trimester (P < 0.05), whereas expression levels of 3β-HSD2 and ARK1C3 were unaltered between GWs 8 and 19. All investigated steroidogenic proteins were expressed in a distinct pattern throughout the investigated period, with most enzymes expressed primarily in the fetal zone, except 3β-HSD1/2, which was expressed mainly in the definitive zone. Abundant steroidogenic enzyme expression was reflected in overall high intra-adrenal tissue concentrations of mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens; cortisol was the most abundant (1071 to 2723 ng/g tissue), and testosterone levels were the lowest (2 to 14 ng/g tissue).
Conclusions: The expression profiles of HFA steroidogenic enzymes are distinct from first to second trimester, with no major differences between male and female samples. Intra-adrenal steroid hormone concentrations confirm that cortisol is produced throughout first and second trimesters, suggesting continued regulation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis during this entire period.
Copyright © 2019 Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Novoselova TV, Jackson D, Campbell DC, Clark AJL, Chan LF. Melanocortin receptor accessory proteins in adrenal gland physiology and beyond. J Endocrinol. 2013;217(1):R1–R11. - PubMed
-
- Ekström L, Rane A. Genetic variation, expression and ontogeny of sulfotransferase SULT2A1 in humans. Pharmacogenomics J. 2015;15(4):293–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

