Ventx1.1 as a Direct Repressor of Early Neural Gene zic3 in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 30590909
- PMCID: PMC6315313
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2018.0341
Ventx1.1 as a Direct Repressor of Early Neural Gene zic3 in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
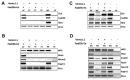
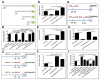
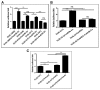
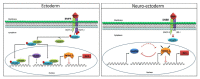
From Xenopus embryo studies, the BMP4/Smad1-targeted gene circuit is a key signaling pathway for specifying the cell fate between the ectoderm and neuro-ectoderm as well as the ventral and dorsal mesoderm. In this context, several BMP4/Smad1 target transcriptional factors have been identified as repressors of the neuro-ectoderm. However, none of these direct target transcription factors in this pathway, including GATA1b, Msx1 and Ventx1.1 have yet been proven as direct repressors of early neuro-ectodermal gene expression. In order to demonstrate that Ventx1.1 is a direct repressor of neuro-ectoderm genes, a genome-wide Xenopus ChIP-Seq of Ventx1.1 was performed. In this study, we demonstrated that Ventx1.1 bound to the Ventx1.1 response cis-acting element 1 and 2 (VRE1 and VRE2) on the promoter for zic3, which is a key early neuro-ectoderm gene, and this Ventx1.1 binding led to repression of zic3 transcription. Site-directed mutagenesis of VRE1 and VRE2 within zic3 promoter completely abolished the repression caused by Ventx1.1. In addition, we found both the positive and negative regulation of zic3 promoter activity by FoxD5b and Xcad2, respectively, and that these occur through the VREs and via modulation of Ventx1.1 levels. Taken together, the results demonstrate that the BMP4/Smad1 target gene, Ventx1.1, is a direct repressor of neuro-ectodermal gene zic3 during early Xenopus embryogenesis.
Keywords: Ventx1.1; Xenopus; neurogenesis; transcriptional regulation; zic3.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two Homeobox Transcription Factors, Goosecoid and Ventx1.1, Oppositely Regulate Chordin Transcription in Xenopus Gastrula Embryos.Cells. 2023 Mar 11;12(6):874. doi: 10.3390/cells12060874. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980215 Free PMC article.
-
Ventx1.1 competes with a transcriptional activator Xcad2 to regulate negatively its own expression.BMB Rep. 2019 Jun;52(6):403-408. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.6.085. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 31068250 Free PMC article.
-
Foxd4l1.1 negatively regulates transcription of neural repressor ventx1.1 during neuroectoderm formation in Xenopus embryos.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 8;10(1):16780. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73662-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33033315 Free PMC article.
-
Bmp4 Synexpression Gene, Sizzled, Transcription Is Collectively Modulated by Smad1 and Ventx1.1/Ventx2.1 in Early Xenopus Embryos.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 1;23(21):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113335. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362118 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium transients and calcium signalling during early neurogenesis in the amphibian embryo Xenopus laevis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Nov;1763(11):1184-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.005. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16987559 Review.
Cited by
-
Two Homeobox Transcription Factors, Goosecoid and Ventx1.1, Oppositely Regulate Chordin Transcription in Xenopus Gastrula Embryos.Cells. 2023 Mar 11;12(6):874. doi: 10.3390/cells12060874. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36980215 Free PMC article.
-
Bmp Signal Gradient Modulates Convergent Cell Movement via Xarhgef3.2 during Gastrulation of Xenopus Embryos.Cells. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):44. doi: 10.3390/cells11010044. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011606 Free PMC article.
-
Foxd4l1.1 Negatively Regulates Chordin Transcription in Neuroectoderm of Xenopus Gastrula.Cells. 2021 Oct 17;10(10):2779. doi: 10.3390/cells10102779. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685759 Free PMC article.
-
Goosecoid Controls Neuroectoderm Specification via Dual Circuits of Direct Repression and Indirect Stimulation in Xenopus Embryos.Mol Cells. 2021 Oct 31;44(10):723-735. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0055. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 34711690 Free PMC article.
-
Ventx Family and Its Functional Similarities with Nanog: Involvement in Embryonic Development and Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 1;23(5):2741. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052741. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dale L., Jones C.M. BMP signalling in early Xenopus development. Bioessays. 1999;21:751–760. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

