Krüppel like factor 6 splice variant 1 (KLF6-SV1) overexpression recruits macrophages to participate in lung cancer metastasis by up-regulating TWIST1
- PMID: 30590988
- PMCID: PMC6605981
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1550570
Krüppel like factor 6 splice variant 1 (KLF6-SV1) overexpression recruits macrophages to participate in lung cancer metastasis by up-regulating TWIST1
Abstract
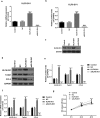
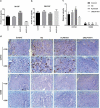
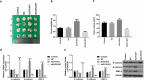
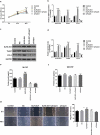
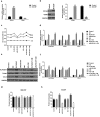
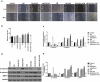
The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism by which KLF6-SV1 promoted lung cancer metastasis through tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Plasmid transfection was used to construct cells that upregulated or silenced gene. Tumor-bearing mouse model was established using A549 cells. SP staining was performed to detect the CD163 and CD68. Six-well plates and Transwell chamber were used for co-culture of lung cancer A549 cells and macrophages. CCK-8 and Transwell assay were applied to detected the cell viability and migration respectively. Protein and mRNA were tested by Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).KLF6-SV1 overexpression promoted the expression levels of TWIST1 and CCL2, and also induce macrophage polarization to M2 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In vitro experiments showed that KLF6-SV1 might regulate the migration of lung cancer cells by regulating the expression of TWIST1 and CCL-2. M2 macrophages did not affect the expression of KLF6-SV1, TWIST1 and CCL-2. The co-culture system could up-regulate the EMT of A549 cells.Overexpression of KLF6-SV1 promoted the expression of TWIST1 and CCL2, and up-regulation of TWIST1 expression might promote the infiltration of M2 macrophages, which promoted the involvement of EMT in the metastasis of lung cancer cells.
Keywords: Krüppel like factor 6; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; lung cancer; non-small cell lung cancer; tumor-associated macrophage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of Krüppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 in the development, diagnosis, and possible treatment strategies for non-small cell lung cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 15;12(10):4468-4482. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36381325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small interfering RNA targeting the KLF6 splice variant, KLF6-SV1, as gene therapy for gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2011 Oct;14(4):339-52. doi: 10.1007/s10120-011-0049-x. Epub 2011 May 3. Gastric Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21538018
-
KLF6-SV1 drives breast cancer metastasis and is associated with poor survival.Sci Transl Med. 2013 Jan 23;5(169):169ra12. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004688. Sci Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23345610 Free PMC article.
-
TWIST1 upregulates miR-214 to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jul;42(1):461-470. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3630. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29693173
-
The role of KLF6 and its splice variants in cancer therapy.Drug Resist Updat. 2009 Feb-Apr;12(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Dec 18. Drug Resist Updat. 2009. PMID: 19097929 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Krüppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 in the development, diagnosis, and possible treatment strategies for non-small cell lung cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 15;12(10):4468-4482. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36381325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-associated macrophages: an effective player of the tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 16;14:1295257. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1295257. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38035101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological and toxicological roles of Kruppel-like factors (KLFs) in the cardiovascular system: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 26;52(1):506. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10613-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40418318 Review.
-
Identification and Validation of a Stromal EMT Related LncRNA Signature as a Potential Marker to Predict Bladder Cancer Outcome.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 4;11:620674. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.620674. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33747932 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-487a derived from m2 macrophage promotes the progression of gastric cancer.Cell Cycle. 2021 Feb;20(4):434-444. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1878326. Epub 2021 Jan 31. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33522393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meguid RA, Hooker CM, Harris J, Xu L, Westra WH, Sherwood JT, Sussman M, Cattaneo SM, Shin J, Cox S, et al. Long-term survival outcomes by smoking status in surgical and nonsurgical patients with non-small cell lung cancer: comparing never smokers and current smokers. Chest. 2010;138:500–509. doi:10.1378/chest.08-2991. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Voltolini L, Bongiolatti S, Luzzi L, Bargagli E, Fossi A, Ghiribelli C, Rottoli P, Gotti G.. Impact of interstitial lung disease on short-term and long-term survival of patients undergoing surgery for non-small-cell lung cancer: analysis of risk factors. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013;43:e17–23. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezs560. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
