Prognostic and clinicopathological value of FoxM1 expression in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30593202
- PMCID: PMC6314739
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013899
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of FoxM1 expression in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The study aims to assess the relationship between FoxM1 expression and clinicopathological parameters and prognosis of patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer (CRC) by summarizing the studies included.
Methods: PubMed, EMBASE, The Cochrane Library and other sources were searched for relative studies. Odds ratio (OR) and confidence interval (CI) were used to assess association between FoxM1 expression and clinical parameters and prognosis of CRC patients.
Results: Eight studies were included in the final analysis, with 1149 CRC patients. The outcome revealed that expression of FoxM1 was associated with lymph node metastasis (OR = 0.33, 95%CI = 0.19-0.62, P < .001), distant metastasis (OR = 0.35, 95%CI = 0.24-0.46, P < .001) and tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage (OR = 0.45, 95%CI = 0.29-0.72, P < .001). Meanwhile, reduced FoxM1 expression indicated higher 5-year survival rate (OR = 0.38, 95%CI = 0.18-0.78, P = .01). Expression of FoxM1 was also increased obviously in CRC tissues (OR = 13.04, 95%CI = 4.07-41.71, P < .001).
Conclusion: This pooled analysis indicated that FoxM1 expression related to lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, TNM stage and poor prognosis of the CRC patients.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures

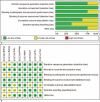


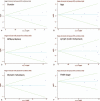

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Shimada H, Tanaka K, Endou I, et al. Treatment for colorectal liver metastases: a review. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2009;394:973–83. - PubMed
-
- Ning Z, Wang A, Liang J, et al. USP22 promotes the G1/S phase transition by upregulating FoxM1 expression via beta-catenin nuclear localization and is associated with poor prognosis in stage II pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol 2014;45:1594–608. - PubMed
-
- Bella L, Zona S, Nestal de Moraes G, et al. FOXM1: a key oncofoetal transcription factor in health and disease. Semin Cancer Biol 2014;29:32–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

