Different clinical predictors of aspiration pneumonia in dysphagic stroke patients related to stroke lesion: A STROBE-complaint retrospective study
- PMID: 30593222
- PMCID: PMC6314729
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013968
Different clinical predictors of aspiration pneumonia in dysphagic stroke patients related to stroke lesion: A STROBE-complaint retrospective study
Abstract
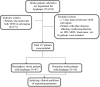
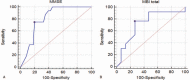
Although stroke is one of the most common causes of dysphagia, no studies have investigated the radionuclide salivagram as a predictor of aspiration pneumonia in patients with stroke. In addition, few researches on the risk factors of aspiration pneumonia in patients with subacute and chronic stroke undergoing rehabilitation in the rehabilitation unit have been rarely conducted. In this study, therefore, we investigated whether a radionuclide salivagram could predict aspiration pneumonia, and tried to find other clinical factors that may be helpful in predicting aspiration pneumonia in stroke patients undergoing rehabilitation in the rehabilitation department.From March 2013 and January 2018, a retrospective review of the medical records of 1182 subacute and chronic stroke patients who were admitted to rehabilitation department (South Korea) was carried out. We included 117 stroke patients with swallowing difficulties who were admitted to our rehabilitation department and satisfied our criteria retrospectively. Stroke lesion, the degree of paralysis, sex, age, onset duration, feeding methods, the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), the Global Deterioration Scale (GDS), the presence of aspiration in VFSS or salivagram, the penetration-aspiration scale (PAS), and the total score of the Modified Barthel Index (MBI) were investigated by reviewing medical records.To evaluate the predictor of aspiration pneumonia for patients with stroke, multivariate logistic regression analysis with forward stepwise was performed. In the results of this study, only MMSE was significant as a clinical predictor, but not aspiration in VFSS or salivagram in multivariate analysis of supratentorial stroke patients (OR, 0.895) (95% CI, 0.830-964). In multivariate analysis of infratentorial stroke patients, combined results of salivagram and VFSS (aspiration in a salivagram or VFSS) (OR, 0.956) (95% CI, 0.919-995), and total MBI scores were significant as clinical predictors (OR, 24.882) (95% CI, 1.298-477.143).In conclusion, MMSE can be a clinical predictor of the occurrence of aspiration pneumonia in patients with supratentorial stroke. In contrast, total MBI score and combined results of a salivagram and VFSS can be clinical predictors of the occurrence of aspiration pneumonia in patients with infratentorial stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Katzan IL, Cebul RD, Husak SH, et al. The effect of pneumonia on mortality among patients hospitalized for acute stroke. Neurology 2003;60:620–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

