Blocking NF-κB Activation in Ly6c+ Monocytes Attenuates Necrotizing Enterocolitis
- PMID: 30593820
- PMCID: PMC6412404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.11.015
Blocking NF-κB Activation in Ly6c+ Monocytes Attenuates Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Abstract
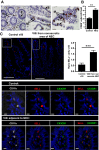
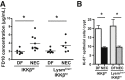
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating disease affecting premature infants with intestinal inflammation and necrosis. The neonatal intestinal inflammatory response is rich in macrophages, and blood monocyte count is low in human NEC. We previously found that NF-κB mediates the intestinal injury in experimental NEC. However, the role of NF-κB in myeloid cells during NEC remains unclear. Herein, inhibitor of kappaB kinase β (IKKβ), a critical kinase mediating NF-κB activation, was deleted in lysozyme M (Lysm)-expressing cells, which were found to be Cd11b+Ly6c+ monocytes but not Cd11b+Ly6c- macrophages in the dam-fed neonatal mouse intestine. NEC induced differentiation of monocytes into intestinal macrophages and up-regulation of monocyte recruitment genes (eg, L-selectin) in the macrophage compartment in wild-type mice, but not in pups with IKKβ deletion in Lysm+ cells. Thus, NF-κB is required for NEC-induced monocyte activation, recruitment, and differentiation in neonatal intestines. Furthermore, pups with Lysm-IKKβ deletion had improved survival and decreased incidence of severe NEC compared with littermate controls. Decreased NEC severity was not associated with an improved intestinal barrier. In contrast, NEC was unabated in mice with IKKβ deletion in intestinal epithelial cells. Together, these data suggest that recruitment of Ly6c+ monocytes into the intestine, NF-κB activation in these cells, and differentiation of Ly6c+ monocytes into macrophages are critical cellular and molecular events in NEC development to promote disease.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNF31-mediated IKKα ubiquitination aggravates inflammation and intestinal injury through regulating NF-κB activation in human and mouse neonates.Life Sci. 2024 Sep 1;352:122893. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122893. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38971367
-
NF-κB inactivation attenuates the M1 macrophage polarization in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis by glutaredoxin-1 deficiency.Cell Biol Int. 2022 Nov;46(11):1886-1899. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11861. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Cell Biol Int. 2022. PMID: 35870170
-
Smad7 interrupts TGF-β signaling in intestinal macrophages and promotes inflammatory activation of these cells during necrotizing enterocolitis.Pediatr Res. 2016 Jun;79(6):951-61. doi: 10.1038/pr.2016.18. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Pediatr Res. 2016. PMID: 26859364 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B in intestinal protection and destruction.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009 Mar;25(2):92-9. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e328324f857. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19528876 Review.
-
Severe anemia predisposes very premature infants to transfusion-associated necrotizing enterocolitis.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2025 Mar;30(1):101615. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2025.101615. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2025. PMID: 40059009 Review.
Cited by
-
Feeding Formula Eliminates the Necessity of Bacterial Dysbiosis and Induces Inflammation and Injury in the Paneth Cell Disruption Murine NEC Model in an Osmolality-Dependent Manner.Nutrients. 2020 Mar 26;12(4):900. doi: 10.3390/nu12040900. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32224880 Free PMC article.
-
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: LPS/TLR4-Induced Crosstalk Between Canonical TGF-β/Wnt/β-Catenin Pathways and PPARγ.Front Pediatr. 2021 Oct 12;9:713344. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.713344. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34712628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression of OLFM4 and lysozyme during necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates: an observational research study.BMC Pediatr. 2022 Apr 11;22(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12887-022-03260-y. BMC Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35410162 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Glycosaminoglycans in Protection from Neonatal Necrotizing Enterocolitis: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 20;12(2):546. doi: 10.3390/nu12020546. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32093194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction of absolute monocyte counts is associated with the severity of preterm necrotizing enterocolitis.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2023 Sep-Oct;99(5):449-455. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2023.02.006. Epub 2023 Apr 2. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2023. PMID: 37015323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma R., Tepas J.J., 3rd, Hudak M.L., Mollitt D.L., Wludyka P.S., Teng R.J., Premachandra B.R. Neonatal gut barrier and multiple organ failure: role of endotoxin and proinflammatory cytokines in sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:454–461. - PubMed
-
- MohanKumar K., Kaza N., Jagadeeswaran R., Garzon S.A., Bansal A., Kurundkar A.R., Namachivayam K., Remon J.I., Bandepalli C.R., Feng X., Weitkamp J.H., Maheshwari A. Gut mucosal injury in neonates is marked by macrophage infiltration in contrast to pleomorphic infiltrates in adult: evidence from an animal model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G93–G102. - PMC - PubMed
-
- He Y.M., Li X., Perego M., Nefedova Y., Kossenkov A.V., Jensen E.A., Kagan V., Liu Y.F., Fu S.Y., Ye Q.J., Zhou Y.H., Wei L., Gabrilovich D.I., Zhou J. Transitory presence of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in neonates is critical for control of inflammation. Nat Med. 2018;24:224–231. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pang Y., Du X., Xu X., Wang M., Li Z. Monocyte activation and inflammation can exacerbate Treg/Th17 imbalance in infants with neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;59:354–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

