Targeting cancer stem cell signature gene SMOC-2 Overcomes chemoresistance and inhibits cell proliferation of endometrial carcinoma
- PMID: 30594556
- PMCID: PMC6412073
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.044
Targeting cancer stem cell signature gene SMOC-2 Overcomes chemoresistance and inhibits cell proliferation of endometrial carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Endometrial cancer is one of the most common gynecological malignancies and has exhibited an increasing incidence rate in recent years. Cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are responsible for tumor growth and chemoresistance, have been confirmed in endometrial cancer. However, it is still challenging to identify endometrial cancer stem cells to then target for therapy.
Methods: Flow cytometry was used to identify the endometrial cancer stem cells. Sphere formation assay, western blotting, qRT-PCR assay, cell viability assay, xenograft assay and immunohistochemistry staining analysis were utilized to evaluate the effect of SPARC-related modular calcium binding 2 (SMOC-2) on the cells proliferation and drug resistance. Cell viability assay, qRT-PCR assay, immunofluorescence staining, Co-IP assay and luciferase reporter gene assay were performed to explore the possible molecular mechanism by which SMOC-2 activates WNT/β-catenin pathway.
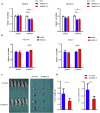
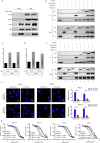
Findings: We found the expression of SPARC-related modular calcium binding 2 (SMOC-2), a member of SPARC family, was higher in endometrial CSCs than that in non-CSCs. SMOC-2 was also more highly expressed in spheres than in monolayer cultures. The silencing of SMOC-2 suppressed cell sphere ability; reduced the expression of the stemness-associated genes SOX2, OCT4 and NANOG; and enhanced chemosensitivity in endometrial cancer cells. By co-culture IP assay, we demonstrated that SMOC-2 directly interacted with WNT receptors (Fzd6 and LRP6), enhanced ligand-receptor interaction with canonical WNT ligands (Wnt3a and Wnt10b), and finally, activated the WNT/β-catenin pathway in endometrial cancer. SMOC-2 expression was closely correlated with CSC markers CD133 and CD44 expression in endometrial cancer tissue.
Interpretation: Taken together, we conclude that SMOC-2 might be a novel endometrial cancer stem cell signature gene and therapeutic target for endometrial cancer. FUND: National Natural Science Foundation of China, Scientific and Technological Innovation Act Program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, Scientific and Technological Innovation Act Program of Fengxian Science and Technology Commission, Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai.
Keywords: Cancer stem cells; Chemoresistance; Endometrial carcinoma; SMOC-2; WNT/β-catenin pathway.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
NANOGP8 is the key regulator of stemness, EMT, Wnt pathway, chemoresistance, and other malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cells.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 24;13(4):e0192436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192436. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29689047 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of the intestinal stem cell signature gene SMOC-2 is required for L1-mediated colon cancer progression.Oncogene. 2016 Feb 4;35(5):549-57. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.127. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25915847
-
Construction and application of a lung cancer stem cell model: antitumor drug screening and molecular mechanism of the inhibitory effects of sanguinarine.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13871-13883. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5152-5. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27485114
-
Pharmacologic Manipulation of Wnt Signaling and Cancer Stem Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1613:463-478. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7027-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28849572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Importance of Cancer Stem Cells and Their Pathways in Endometrial Cancer: A Narrative Review.Cells. 2025 Apr 14;14(8):594. doi: 10.3390/cells14080594. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of a glycolysis-associated multiomics prognostic model for hepatocellular carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Mar 3;13(5):7481-7498. doi: 10.18632/aging.202613. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33686959 Free PMC article.
-
Cinobufotalin powerfully reversed EBV-miR-BART22-induced cisplatin resistance via stimulating MAP2K4 to antagonize non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIA/glycogen synthase 3β/β-catenin signaling pathway.EBioMedicine. 2019 Oct;48:386-404. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.040. Epub 2019 Oct 5. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31594754 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures: The Bridge between In Vitro and In Vivo Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 27;24(15):12046. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512046. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights on the Role of Polyphenols in Combating Cancer Drug Resistance.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 14;11(6):1709. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061709. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Risk Signature with Nine Stemness Index-Associated Genes for Predicting Survival of Patients with Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2021 Mar 6;2021:6653247. doi: 10.1155/2021/6653247. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33747079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre L.A., Bray F., Siegel R.L., Ferlay J., Lortet-Tieulent J., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017 - PubMed
-
- Basil J.B., Goodfellow P.J., Rader J.S., Mutch D.G., Herzog T.J. Clinical significance of microsatellite instability in endometrial carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;89(8):1758–1764. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

