Error Processing and Inhibitory Control in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Meta-analysis Using Statistical Parametric Maps
- PMID: 30595231
- PMCID: PMC6474799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.11.010
Error Processing and Inhibitory Control in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Meta-analysis Using Statistical Parametric Maps
Abstract
Background: Error processing and inhibitory control enable the adjustment of behaviors to meet task demands. Functional magnetic resonance imaging studies report brain activation abnormalities in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) during both processes. However, conclusions are limited by inconsistencies in the literature and small sample sizes. Therefore, the aim here was to perform a meta-analysis of the existing literature using unthresholded statistical maps from previous studies.
Methods: A voxelwise seed-based d mapping meta-analysis was performed using t-maps from studies comparing patients with OCD and healthy control subjects (HCs) during error processing and inhibitory control. For the error processing analysis, 239 patients with OCD (120 male; 79 medicated) and 229 HCs (129 male) were included, while the inhibitory control analysis included 245 patients with OCD (120 male; 91 medicated) and 239 HCs (135 male).
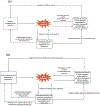
Results: Patients with OCD, relative to HCs, showed longer inhibitory control reaction time (standardized mean difference = 0.20, p = .03, 95% confidence interval = 0.016, 0.393) and more inhibitory control errors (standardized mean difference = 0.22, p = .02, 95% confidence interval = 0.039, 0.399). In the brain, patients showed hyperactivation in the bilateral dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, supplementary motor area, and pre-supplementary motor area as well as right anterior insula/frontal operculum and anterior lateral prefrontal cortex during error processing but showed hypoactivation during inhibitory control in the rostral and ventral anterior cingulate cortices and bilateral thalamus/caudate, as well as the right anterior insula/frontal operculum, supramarginal gyrus, and medial orbitofrontal cortex (all seed-based d mapping z value >2, p < .001).
Conclusions: A hyperactive error processing mechanism in conjunction with impairments in implementing inhibitory control may underlie deficits in stopping unwanted compulsive behaviors in the disorder.
Keywords: Error processing; Inhibitory control; Meta-analysis; OCD; Performance monitoring; fMRI.
Copyright © 2018 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013): Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Norman LJ, Carlisi C, Lukito S, Hart H, Mataix-Cols D, Radua J, Rubia K (2016): Structural and functional brain abnormalities in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: A comparative meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 73: 815–825. - PubMed
-
- Carlisi CO, Norman LJ, Lukito SS, Radua J, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K (2017): Comparative multimodal meta-analysis of structural and functional brain abnormalities in autism spectrum disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 82: 83–102. - PubMed

