Seven-year clinical outcomes in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with biodegradable polymer coated sirolimus-eluting stent: Results from a single-center real-world experience
- PMID: 30595275
- PMCID: PMC6309142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2018.05.014
Seven-year clinical outcomes in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with biodegradable polymer coated sirolimus-eluting stent: Results from a single-center real-world experience
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the present study was to assess seven-year clinical outcomes of biodegradable polymer coated Supralimus sirolimus-eluting stent (S-SES) [Sahajanand Medical Technologies Pvt. Ltd., Surat, India] in real-world patients with coronary artery disease.
Methods: This observational, retrospective study was carried out in all 346 consecutive enrolled patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with the S-SES, between April 2008 and December 2009, at a single center. We analyzed major adverse cardiac events (MACE) [a composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction (MI), target lesion revascularization (TLR) and target vessel revascularization (TVR)] as primary outcomes at seven-year follow-up.
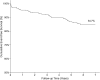
Results: Out of 346 patients, seven-year follow-up was obtained in 327 (94.5%) patients and hence results were analyzed for 327 patients. At seven-year, MACE occurred in 41 (12.5%) patients, consisting of 23 (7.0%) cardiac deaths, 14 (4.3%) TLR, and 4 (1.2%) TVR. The incidence of late stent thrombosis was observed in 3 (0.9%) patients. At follow-up of seven-year, the cumulative event-free survival was found to be 84.7% by Kaplan-Meier method.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated satisfactory and sustained seven-year clinical outcomes as evidenced by the low rates of MACE and ST for the biodegradable polymer coated S-SES.
Keywords: Biodegradable polymer; Coronary artery lesion; Percutaneous coronary intervention; Sirolimus-eluting stent.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved safety and reduction in stent thrombosis associated with biodegradable polymer-based biolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer-based sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease: final 5-year report of the LEADERS (Limus Eluted From A Durable Versus ERodable Stent Coating) randomized, noninferiority trial.JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013 Aug;6(8):777-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.04.011. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013. PMID: 23968698 Clinical Trial.
-
One-year outcomes of a BioMime™ Sirolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System with a biodegradable polymer in all-comers coronary artery disease patients: The meriT-3 study.Indian Heart J. 2016 Sep-Oct;68(5):599-603. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Indian Heart J. 2016. PMID: 27773396 Free PMC article.
-
Three-Year Outcomes of Biodegradable Polymer-Coated Ultra-Thin (60 µm) Sirolimus-Eluting Stents in Real-World Clinical Practice.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2019 May;48(5):150-155. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2019. PMID: 31210252
-
Safety and efficacy of ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer drug-eluting stents: a meta-analysis of randomized trials.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Aug 15;18(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0902-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 30111289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long time clinical outcomes of limus-eluting stent versus paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary artery intervention: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials.Cardiol J. 2014;21(3):211-9. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2014.0004. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Cardiol J. 2014. PMID: 24526500 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of cardiopulmonary fitness parameters in the prognosis of patients with acute coronary syndrome after percutaneous coronary intervention.J Int Med Res. 2020 Aug;48(8):300060520949081. doi: 10.1177/0300060520949081. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32840161 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes and complications of treatment with supraflex stent in patients with coronary artery disease: One-year follow-up.Eur J Transl Myol. 2019 May 22;29(2):8231. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2019.8231. eCollection 2019 May 7. Eur J Transl Myol. 2019. PMID: 31354927 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional ultrathin Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets coated intraocular lens for synergistic photothermal and NIR-controllable rapamycin releasing therapy against posterior capsule opacification.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 30;10:989099. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.989099. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36110318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moses J.W., Leon M.B., Popma J.J. Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1315–1323. - PubMed
-
- Babapulle M.N., Joseph L., Belisle P. A hierarchical Bayesian meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials of drug-eluting stents. Lancet. 2004;364:583–591. - PubMed
-
- Chamie D., Abizaid A., Costa J.R., Jr. Serial angiographic and intravascular ultrasound evaluation to interrogate the presence of late catch-up phenomenon after Cypher(R) sirolimus-eluting stent implantation. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011;27:867–874. - PubMed
-
- Nebeker J.R., Virmani R., Bennett C.L. Hypersensitivity cases associated with drug-eluting coronary stents: a review of available cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports (RADAR) project. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:175–181. - PubMed
-
- Virmani R., Guagliumi G., Farb A. Localized hypersensitivity and late coronary thrombosis secondary to a sirolimus-eluting stent: should we be cautious. Circulation. 2004;109:701–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous