Expansion of Islet-Resident Macrophages Leads to Inflammation Affecting β Cell Proliferation and Function in Obesity
- PMID: 30595478
- PMCID: PMC6701710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.12.003
Expansion of Islet-Resident Macrophages Leads to Inflammation Affecting β Cell Proliferation and Function in Obesity
Abstract
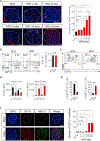
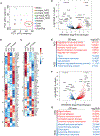
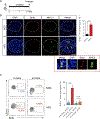
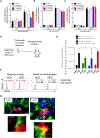
The nature of obesity-associated islet inflammation and its impact on β cell abnormalities remains poorly defined. Here, we explore immune cell components of islet inflammation and define their roles in regulating β cell function and proliferation. Islet inflammation in obese mice is dominated by macrophages. We identify two islet-resident macrophage populations, characterized by their anatomical distributions, distinct phenotypes, and functional properties. Obesity induces the local expansion of resident intra-islet macrophages, independent of recruitment from circulating monocytes. Functionally, intra-islet macrophages impair β cell function in a cell-cell contact-dependent manner. Increased engulfment of β cell insulin secretory granules by intra-islet macrophages in obese mice may contribute to restricting insulin secretion. In contrast, both intra- and peri-islet macrophage populations from obese mice promote β cell proliferation in a PDGFR signaling-dependent manner. Together, these data define distinct roles and mechanisms for islet macrophages in the regulation of islet β cells.
Keywords: islet inflammation; local macrophages proliferation; macrophages; obesity; β cell function; β cell proliferation.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Gaining Weight: Insulin-Eating Islet Macrophages.Immunity. 2019 Jan 15;50(1):13-15. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.12.026. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 30650372
-
Drivers of islet inflammation.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Mar;15(3):128. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0159-9. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30655623 No abstract available.
References
-
- Araújo TG, Oliveira AG, Carvalho BM, Guadagnini D, Protzek AO, Carvalheira JB, Boschero AC, and Saad MJ (2012). Hepatocyte growth factor plays a key role in insulin resistance-associated compensatory mechanisms. Endocrinology 153, 5760–5769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

