Probing the Function of Metazoan Histones with a Systematic Library of H3 and H4 Mutants
- PMID: 30595536
- PMCID: PMC6595499
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.11.047
Probing the Function of Metazoan Histones with a Systematic Library of H3 and H4 Mutants
Abstract
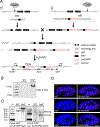
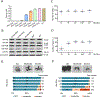
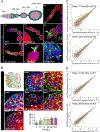
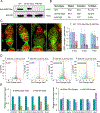
Replication-dependent histone genes often reside in tandemly arrayed gene clusters, hindering systematic loss-of-function analyses. Here, we used CRISPR/Cas9 and the attP/attB double-integration system to alter numbers and sequences of histone genes in their original genomic context in Drosophila melanogaster. As few as 8 copies of the histone gene unit supported embryo development and adult viability, whereas flies with 20 copies were indistinguishable from wild-types. By hierarchical assembly, 40 alanine-substitution mutations (covering all known modified residues in histones H3 and H4) were introduced and characterized. Mutations at multiple residues compromised viability, fertility, and DNA-damage responses. In particular, H4K16 was necessary for expression of male X-linked genes, male viability, and maintenance of ovarian germline stem cells, whereas H3K27 was essential for late embryogenesis. Simplified mosaic analysis showed that H3R26 is required for H3K27 trimethylation. We have developed a powerful strategy and valuable reagents to systematically probe histone functions in D. melanogaster.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Drosophila; FLP-FRT; H4K16; attB-attP; dosage effects; histone mutant library; mosaic system.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nejire/dCBP-mediated histone H3 acetylation during spermatogenesis is essential for male fertility in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 7;13(9):e0203622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203622. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30192860 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific phenotypes of histone H4 point mutants establish dosage compensation as the critical function of H4K16 acetylation in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 26;115(52):13336-13341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817274115. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30530664 Free PMC article.
-
CBP-mediated acetylation of histone H3 lysine 27 antagonizes Drosophila Polycomb silencing.Development. 2009 Sep;136(18):3131-41. doi: 10.1242/dev.037127. Development. 2009. PMID: 19700617 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine 27 of replication-independent histone H3.3 is required for Polycomb target gene silencing but not for gene activation.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jan 30;15(1):e1007932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007932. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 30699116 Free PMC article.
-
Hat1 acetylates histone H4 and modulates the transcriptional program in Drosophila embryogenesis.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 29;9(1):17973. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54497-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31784689 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A powerful and highly efficient PAI-mediated transgenesis approach in Drosophila.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Apr 22;53(8):gkaf317. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf317. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40266685 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for dual roles of histone H3 lysine 4 in antagonizing Polycomb group function and promoting target gene expression.Genes Dev. 2024 Nov 27;38(21-24):1033-1046. doi: 10.1101/gad.352181.124. Genes Dev. 2024. PMID: 39562140 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory genome of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae: integrating chromatin accessibility and gene expression.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021 Jan 20;3(1):lqaa113. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqaa113. eCollection 2021 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33987532 Free PMC article.
-
Redesigning the Drosophila histone gene cluster: an improved genetic platform for spatiotemporal manipulation of histone function.Genetics. 2024 Sep 4;228(1):iyae117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae117. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 39039029 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Roles of H3K4 Methylation in Transcriptional Regulation.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(11):505-515. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2388254. Epub 2024 Aug 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39155435 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Celic I, Masumoto H, Griffith WP, Meluh P, Cotter RJ, Boeke JD, and Verreault A (2006). The sirtuins hst3 and Hst4p preserve genome integrity by controlling histone h3 lysine 56 deacetylation. Curr Biol 16, 1280–1289. - PubMed
-
- Cheung WL, Turner FB, Krishnamoorthy T, Wolner B, Ahn SH, Foley M, Dorsey JA, Peterson CL, Berger SL, and Allis CD (2005). Phosphorylation of histone H4 serine 1 during DNA damage requires casein kinase II in S. cerevisiae. Curr Biol 15, 656–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

