In vitro Research Concerning Effect of Clopidogrel Alone and on Combination with Aspirin and Dypiridamoleon Sedimentation of Erythrocytes
- PMID: 30595849
- PMCID: PMC6286731
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.43.01.02
In vitro Research Concerning Effect of Clopidogrel Alone and on Combination with Aspirin and Dypiridamoleon Sedimentation of Erythrocytes
Abstract
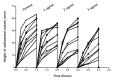
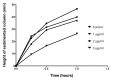
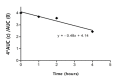
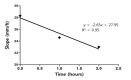
Based on extended theory of Derjaguin, Landau and Overbeeck (xDLVO) concerning aggregation of colloids and biological cells it was hypothesized that platelet antiaggregant agents have to reduce the aggregation of erythrocytes also. Applying Einstein-Stokes theory of sedimentation of spheres in viscous media it was concluded that sedimentation of erythrocytes is in fact sedimentation of aggregates of the approximately same size. Consequently, an expected outcome was that addition of antiaggregants in vitro to blood samples from patients with rheumatic or cardiovascular diseases will be the decrease of erythrocytes sedimentation. Starting from usual practice of dual antiaggregant therapy (aspirin and clopidogrel) effects of clopidogrel were compared with effects of clopidogrel plus small concentrations of aspirine and dipyridamole (smaller that their concentrations in plasma after in vivo administration) in order to put in evidence a possible synergic effect at platelet membrane level. Whole blood (0.8ml) was collected on 0.1ml 1% EDTA and then was added 25 or 50µl normal saline solution of clopidogrel or of the combination acetylosalycilic acid, clopidogrel and dypyridamole. The final concentrations were 1, 2 and µg/ml, of the same order as cumulated concentration of clopidogrel and its metabolites in clinical pharmacokinetics. Experiments were performed on a number of 40 human blood samples obtained from 2 groups of 20 patients. Sedimentation of erythrocytes was recorded using a camera and captured data were stored on a computer. Global analysis evidenced that in presence of antiaggregants the clusters of the sedimentation curves shifted down and into right, indicating a decrease and delay of sedimentation. Initial slopes and extent of sedimentation decreased linearly on clopidogrel concentration within the 1-3µg/ml range. For comparison of mean curves corresponding to different clopidogrel concentrations it was applied a metric from biopharmacy: areas under plasma concentrations curves (AUC) of drugs. The areas under average sedimentation curves decreased linearly at clopidogrel concentration within the 1-3µg/ml range. The same experiments were performed and similar results were obtained with the triple antiaggregant combination (clopidogrel, acetylosalycilic acid and dipyridamole). Apparently, a synergism between the tested antiaggregants appeared at studied concentration but the number of data was not sufficient to prove the statistical significance of the difference between clopidogrel alone and in triple combination.
Keywords: Bioequivalence Metrics; Blood Cells Aggregation; Clopidogrel; Erythrocyte Sedimentation Curves; xDLVO.
Figures






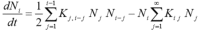
Similar articles
-
Impact of the Chinese herbal medicines on dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel and aspirin: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics outcomes and related mechanisms in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 10;235:100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.01.040. Epub 2019 Jan 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30710735
-
Enhanced antiplatelet effects of clopidogrel plus acetylsalicylic acid compared with acetylsalicylic acid alone or combined with extended-release dipyridamole in healthy volunteers.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005;19(4):214-9. doi: 10.1159/000083885. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005. PMID: 15703464 Clinical Trial.
-
Antiplatelet profiles of the fixed-dose combination of extended-release dipyridamole and low-dose aspirin compared with clopidogrel with or without aspirin in patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of transient ischemic attack: a randomized, single-blind, 30-day trial.Clin Ther. 2008 Feb;30(2):249-59. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.02.006. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18343263 Clinical Trial.
-
Combination antiplatelet agents for secondary prevention of ischemic stroke.Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Oct;28(10):1233-42. doi: 10.1592/phco.28.10.1233. Pharmacotherapy. 2008. PMID: 18823219 Review.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of antiplatelet agents used in the secondary prevention of stroke.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003;42(10):909-20. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200342100-00003. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2003. PMID: 12885264 Review.
References
-
- von Beckerath N, Taubert D, Pogatsa-Murray G, Schömig E, Kastrati A, Schömig A. Absorption, metabolization, and antiplatelet effects of 300-, 600-, and 900-mg loading doses of clopidogrel: results of the ISAR-CHOICE (Intracoronary Stenting and Antithrombotic Regimen: Choose Between 3 High Oral Doses for Immediate Clopidogrel Effect) Trial. Circulation. 2005;112(19):2946–2950. - PubMed
-
- Tantry US, Bliden KP, Gurbel PA. Resistance to antiplatelet drugs: current status and future research. Expert OpinPharmacother. 2005;6:2027–2027. - PubMed
-
- Matetzky S, Shenkman B, Guetta V, Shechter M, Beinart R, Goldenberg I, Novikov I, Pres H, Savion N, Varon D, Hod H. Clopidogrel resistance is associated with increased risk of recurrent atherothrombotic events in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109(25):3171–3175. - PubMed
-
- Sibbing D, Braun S, Morath T, Mehilli J, Vogt W, Schömig A, Kastrati A, von Beckerath N. Platelet reactivity after clopidogrel treatment assessed with point-of-care analysis and early drug-eluting stent thrombosis. J Am CollCardiol. 2009;53(10):849–858. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
