Case Presentation of Soft Tissue Defect after Bimalleolar Fracture Osteosynthesis
- PMID: 30595907
- PMCID: PMC6286448
- DOI: 10.12865/CHSJ.43.04.16
Case Presentation of Soft Tissue Defect after Bimalleolar Fracture Osteosynthesis
Abstract
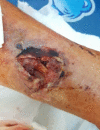
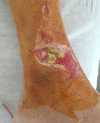
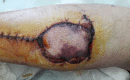
A 59-year-old patient presented in the ER with wound dehiscence and skin necrosis on the right ankle, with osteosynthesis implant visible, after open reduction and fixation with plate and screws, performed abroad, 16 days prior to the presentation, for a bimalleolar fracture. The patient was admitted to the plastic surgery department, where surgical debridement of the necrotic tissue was initially performed. Postoperatively, the patient was treated with Negative-pressure wound therapy (VAC dressing) and Platelet rich plasma (PRP) therapy. Upon obtaining granulation tissue without signs of infection, a sural fasciocutaneous flap was performed to cover the skin defect. Proper graft integration and healing was observed.
Keywords: infection; negative-pressure wound therapy; osteosynthesis; platelet-rich plasma; tissue grafts.
Figures
References
-
- Venturi ML, Attinger CE, Mesbahi AN, Hess CL, Graw KS. Mechanisms and clinical applications of the vacuum-assisted closure (vAC) Device: a review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2005;6(3):185–194. - PubMed
-
- Webb LX. New techniques in wound management: vacuumassisted wound closure. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002;10(5):303–311. - PubMed
-
- Argenta LC, Morykwas MJ. Vacuum-assisted closure: a new method for wound control and treatment: clinical experience. Ann Plast Surg. 1997;38(6):563–576. - PubMed
-
- Waldvogel FA, Medoff G, Swartz MN. Osteomyelitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects. N Engl J Med. 1970;282:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Fears RL, Gleis GE, Seligson D. Skeletal Trauma. 2. Timisoara: PA: WB Saunders Co; 1998. Diagnosis and treatment of complications.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials