LC and LC-MS/MS studies for the identification and characterization of degradation products of acebutolol
- PMID: 30595941
- PMCID: PMC6308026
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2018.03.001
LC and LC-MS/MS studies for the identification and characterization of degradation products of acebutolol
Abstract
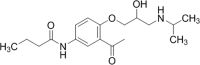
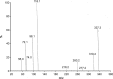
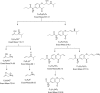
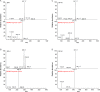
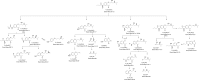
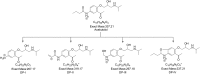
The aim of the present investigation was to demonstrate an approach involving use of liquid chromatography (LC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to separate, identify and characterize very small quantities of degradation products (DPs) of acebutolol without their isolation from the reaction mixtures. The drug was subjected to oxidative, hydrolytic, thermal and photolytic stress conditions as per International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guideline Q1A(R2). Among all the stress conditions the drug was found to be labile in hydrolytic (acidic & basic) and photolytic stress conditions, while it was stable in water-induced hydrolysis, oxidative and thermal stress conditions. A total of four degradation products were formed. A C18 column was employed for the separation of all the DPs on a gradient mode by using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). All the DPs were characterized with the help of their fragmentation pattern and the masses obtained upon LC-MS/MS and MSn analysis. All the hitherto unknown degradation products were identified as 1-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)-5-(amino)phenyl)ethanone (DP-I), N-(4-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)-3-acetylphenyl)acrylamide (DP-II), 1-(2-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)-5-(hydroxymethylamino)phenyl)ethanone (DP-III) and 1-(6-(2-hydroxy-3-(isopropylamino)propoxy)-2,3-dihydro-2-propylbenzo[d]oxazol-5-yl)ethanone (DP-IV). Finally the in-silico carcinogenicity and hepatotoxicity predictions of the drug and all the DPs were performed by using toxicity prediction softwares viz., TOPKAT, LAZAR and Discovery Studio ADMET. The results of in-silico toxicity studies revealed that acebutolol (0.967) and DP-I (0.986) were found to be carcinogenic, while acebutolol (0.490) and DP-IV (0.437) were found to be hepatotoxic.
Keywords: Acebutolol; Degradation pathway; In-silico toxicity; LC; LC–MS/MS; Stress testing.
Figures

References
-
- Moffat A.C., Osselton M.D., Widdop B. Pharmaceutical Press; London: 2005. Clarke’s Analysis of Drugs and Poisons. : 569.
-
- Jiang H., Randlett C., Junga H. Using supported liquid extraction together with cellobiohydrolase chiral stationary phases-based liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry for enantioselective determination of acebutolol and its active metabolite diacetolol in spiked human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B. 2009;877:173–180. - PubMed
-
- Szymura-Oleksiak J., Walczak M., Bojarski J. Enantioselective high performance liquid chromatographic assay of acebutolol and its active metabolite diacetolol in human serum. Chirality. 1999;11:267–271. - PubMed
-
- Miller R.B. A validated, high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of acebutolol and diacetolol in human plasma. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1992;15:3233–3245.
-
- Piquette-Miller M., Foster R.T., Pasutto F.M. Stereospecific high-performance liquid chromatographic assay of acebutolol in human plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. 1990;526:129–137. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

