Hepatoprotective effects of Berberis vulgaris leaf extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 30596119
- PMCID: PMC6282695
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_48_17
Hepatoprotective effects of Berberis vulgaris leaf extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats
Abstract
Introduction: Hepatic sickness is a serious problem for human health. The researchers are interested in using medicinal plants including barberry to cure many of these sicknesses. In this study, the effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Berberis vulgaris leaf on hepatic protection was assessed in rats.
Materials and methods: Forty healthy male Wistar rats were divided randomly into five groups (n = 8): Group 1 (healthy control), intraperitoneal injection of olive oil; Group 2 (hepatotoxic control), intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride and daily gavage of distilled water; and testing groups, intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride along with daily gavage of B. vulgaris leaf extract 40, 80, and 120 mg/kg of weight, respectively. After 6 weeks, the following were checked: enzyme level of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), as well as serum level of total protein (TP), albumin (ALB), and histopathological status of the liver.
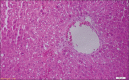
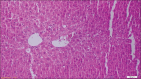
Results: The level of AST, ALP, and ALT was increased to 109 (IU/L), 95(IU/L), and 71(IU/L), respectively, in hepatotoxic control group than healthy control group, and there was a decrease of 0.86 (g/dl) and 0.04 (g/dl) in TP and ALB levels, respectively. The B. vulgaris extract in every three doses caused a significant decrease in hepatic enzymes level. However, the TP had a significant increase in 80 and 120 mg/kg of body weight. Regarding ALB, there was no significant difference among these groups. The histopathological results were not conformed to biochemical findings.
Conclusion: Using the appropriate dose of B. vulgaris leaf extract can help the improvement of laboratory symptoms of fatty liver.
Keywords: Alanine aminotransferase; Berberis vulgaris; alkaline phosphatase; aspartate aminotransferase; carbon tetrachloride; hepatic toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pharmacological safety evaluation of a traditional herbal medicine "Zereshk-e-Saghir" and assessment of its hepatoprotective effects on carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic damage in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 22;190:387-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.043. Epub 2016 Jul 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27426508
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Stachys pilifera ethanol extract in carbon tetrachloride-induce hepatotoxicity in rats.Pharm Biol. 2017 Dec;55(1):1389-1393. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2017.1302484. Pharm Biol. 2017. PMID: 28317417 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Rosa canina fruit extract against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in rat.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2016 Mar-Apr;6(2):181-8. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2016. PMID: 27222831 Free PMC article.
-
A quick overview on some aspects of endocrinological and therapeutic effects of Berberis vulgaris L.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015 Nov-Dec;5(6):485-97. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2015. PMID: 26693406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicology effects of Berberis vulgaris (barberry) and its active constituent, berberine: a review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017 May;20(5):516-529. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2017.8676. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28656087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Meriania hexamera Sprague by Targeting Syk Kinase in NF-κB Signaling.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;12(17):3044. doi: 10.3390/plants12173044. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687291 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Roles and Key Mechanisms of Hawthorn Extract against Various Liver Diseases.Nutrients. 2022 Feb 18;14(4):867. doi: 10.3390/nu14040867. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35215517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adesanoye OA, Farombi EO. Hepatoprotective effects of Vernonia amygdalina (astereaceae) in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2010;62:197–206. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee M, Sarkar K, Sil PC. Herbal (Phyllanthus niruri) protein isolate protects liver from nimesulide induced oxidative stress. Pathophysiology. 2006;13:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed B, Alam T, Khan SA. Hepatoprotective activity of Luffa echinata fruits. J Ethnopharmacol. 2001;76:187–9. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandra Setty S, Quereshi AA, Viswanath Swamy AH, Patil T, Prakash T, Prabhu K, et al. Hepatoprotective activity of Calotropis procera flowers against paracetamol-induced hepatic injury in rats. Fitoterapia. 2007;78:451–4. - PubMed
-
- Liang D1, Zhou Q Faure P, Lafond JL. Analysis of Free Radicals in Biological Systems. Basel: Birkhauser; 1995. Measurement of plasma sulfhydryl and carbonyl groups as a possible indicator of protein oxidation.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

