Trichostatin A Shows Transient Protection from Chronic Alcohol-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells
- PMID: 30596124
- PMCID: PMC6309403
- DOI: 10.4172/2329-6488.1000316
Trichostatin A Shows Transient Protection from Chronic Alcohol-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to understand whether histone deacetylase (HDACs) inhibitor Trichostatin A or TSA can block and/or reverse chronic alcohol exposure-induced ROS in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells (MDDCs). Additionally, since nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) is a known regulator of antioxidant responses, we studied the effects of alcohol and TSA on ROS production and modulation of Nrf2 by MDDCs.
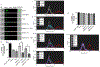
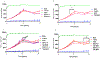
Methods: Intra-cellular, extra-cellular, and total ROS levels were measured in MDDCs treated chronically with alcohol (0.1 and 0.2 % EtOH) using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCF-DA) followed by detection of ROS in microplate reader and imaging flow cytometer. Nrf2 expression was analyzed by qRT- PCR and western blot. In addition, NFE2L2 (Nrf2), class I HDAC genes HDAC1, HDAC2, and histone acetyltransferase genes KAT5 were analyzed in silico using the GeneMania prediction server.
Results: Our results confirmed alcohol's ability to increase intracellular ROS levels in MDDCs within minutes of treatment. Our findings have also demonstrated, for the first time, that TSA has a transient protective effect on MDDCs treated chronically with alcohol since the ability of TSA to reduce intracellular ROS levels is only detected up to 15 minutes post-chronic alcohol treatment with no significant protective effects by 10 hours. In addition, chronic alcohol treatment was able to increase the expression of the antioxidant regulator Nrf2 in a dose dependent manner, and the effect of the higher amount of alcohol (0.2%) on Nrf2 gene expression was significantly enhanced by TSA.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that TSA has a transient protective effect against ROS induced by chronic alcohol exposure of human MDDCs and chronic long-term exposure of MDDCs with alcohol and TSA induces cellular toxicity. It also highlights imaging flow cytometry as a novel tool to detect intracellular ROS levels. Overall, the effect of TSA might be mediated through Nrf2; however, further studies are needed to fully understand the molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: Human dendritic cells; Imaging flow cytometry; Oxidative stress; Reactive oxygen species; Trichostatin A.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
