USAGE OF A RAPID DIAGNOSTIC TEST FOR MALARIA IN CHILDREN
- PMID: 30596193
- PMCID: PMC6305079
- DOI: 10.21010/ajid.v13i1.3
USAGE OF A RAPID DIAGNOSTIC TEST FOR MALARIA IN CHILDREN
Abstract
Background: Malaria is still the primary cause of pediatric deaths. The efficient management of pediatric malaria requires its rapid and accurate diagnosis. To fulfill this requirement, rapid diagnostic tests have been developed, but their evaluation before commercialization is never exhaustive. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of a rapid diagnostic test (SD Bioline Malaria Antigen P.f/Pan) to diagnose malaria in children.
Materials and methods: Testing was conducted on children aged between 6 months and 15 years who were examined at the "Centre Mère Enfant (CME) of the "Chantal Biya" Foundation (FCB). as a result of fever. Enrollment took place from April to October 2014. All children presenting with fever were sampled (3ml of blood). These blood samples were tested for malaria using microscopy on a thick blood smear and by a rapid diagnostic test (RDT) SD Bioline Malariae Antigen P.f/Pan.
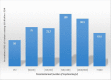
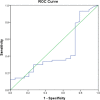
Results: A total of 249 children were enrolled in this study. Malaria presence as determined by microscopy and by RDT was 30.9% and 58.2% respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values compared to microscopy were: 75; 48.8; 39, and 81.6%. With these performances, the malaria SD Bioline rapid test presents lower values compared to WHO recommendations for rapid tests (sensitivity > 95%) in children.
Conclusion: SD Bioline Malaria Antigen P.f/Pan test should only be used in peripheral health structures that lack resources, and should be aided by clinical diagnosis.
Keywords: Keyword: Malaria; Microscopy; Performance; Rapid diagnostic test; thick blood smear.
Figures
References
-
- Ali IM, Bigoga JD, Forsah DA, Cho-Ngwa F, Tchinda V, Moor VA, Fogako J, Nyongalema P, Nkoa T, Same-Ekobo A, Mbede J, Fondjo E, Mbacham W.F, Leke R.G.F. Field evaluation of the 22 rapid diagnostic tests for community management of malaria with artemisinin combination therapy in Cameroon. Malar J. 2016;15:31. DOI 10.1186/s12936-016-1085-0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amos F. Performances diagnostiques du test rapide Optimal-IT: Place de la Biologie moléculaire dans l'évaluation du polymorphisme génétique du lactate déshydrogénase (LDH) de P. falciparum. Thèse de doctorat en pharmacie, Universitéde Bamako, Mali. 2005:144.
-
- Akotet B.M.K, Nkare CA, Mbouoronde OC, Mawili-Mboumba DP. Performances of SD Bioline Malaria Ag-P.F/Pan RDT for the Diagnosis of Malaria in Febrile Patients Living In Gabon, Central Africa. Malar Chemoth Cont Elimination. 2014;3:125. doi:10.4172/2090-2778.1000125.
-
- Baker J, McCarthy J, Gatton M, Kyle DE, Belizario V, Luchavez J, Bell D, Cheng Q. Genetic diversity of Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (PfHRP2) and its effect on the performance of PfHRP2-based rapid diagnostic tests. J Infect Dis. 2005;192:870–877. - PubMed
-
- Bartoloni A, Sabatinelli G, Benucci M. Performance of two rapid tests for Plasmodium falciparum malaria in patients with rheumatoid factors. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1075. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous