Deconstructing Cell-Free Extract Preparation for in Vitro Activation of Transcriptional Genetic Circuitry
- PMID: 30596483
- PMCID: PMC6584022
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00430
Deconstructing Cell-Free Extract Preparation for in Vitro Activation of Transcriptional Genetic Circuitry
Abstract
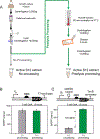
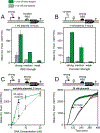
Recent advances in cell-free gene expression (CFE) systems have enabled their use for a host of synthetic biology applications, particularly for rapid prototyping of genetic circuits and biosensors. Despite the proliferation of cell-free protein synthesis platforms, the large number of currently existing protocols for making CFE extracts muddles the collective understanding of how the extract preparation method affects its functionality. A key aspect of extract performance relevant to many applications is the activity of the native host transcriptional machinery that can mediate protein synthesis. However, protein yields from genes transcribed in vitro by the native Escherichia coli RNA polymerase are variable for different extract preparation techniques, and specifically low in some conventional crude extracts originally optimized for expression by the bacteriophage transcriptional machinery. Here, we show that cell-free expression of genes under bacterial σ70 promoters is constrained by the rate of transcription in crude extracts, and that processing the extract with a ribosomal runoff reaction and subsequent dialysis alleviates this constraint. Surprisingly, these processing steps only enhance protein synthesis in genes under native regulation, indicating that the translation rate is unaffected. We further investigate the role of other common extract preparation process variants on extract performance and demonstrate that bacterial transcription is inhibited by including glucose in the growth culture but is unaffected by flash-freezing the cell pellet prior to lysis. Our final streamlined and detailed protocol for preparing extract by sonication generates extract that facilitates expression from a diverse set of sensing modalities including protein and RNA regulators. We anticipate that this work will clarify the methodology for generating CFE extracts that are active for biosensing using native transcriptional machinery and will encourage the further proliferation of cell-free gene expression technology for new applications.
Keywords: CFE; CFPS; TX-TL; cell extract; cell-free synthetic biology; endogenous transcription; genetic circuitry; in vitro protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
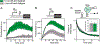


Similar articles
-
Protocols for implementing an Escherichia coli based TX-TL cell-free expression system for synthetic biology.J Vis Exp. 2013 Sep 16;(79):e50762. doi: 10.3791/50762. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 24084388 Free PMC article.
-
Simple Extract Preparation Methods for E. coli-Based Cell-Free Expression.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2433:51-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1998-8_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34985736
-
Establishing a High-Yield Bacillus subtilis-Based Cell-Free Protein Synthesis System for In Vitro Prototyping and Natural Product Biosynthesis.ACS Synth Biol. 2025 Apr 18;14(4):1288-1297. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.5c00021. Epub 2025 Apr 9. ACS Synth Biol. 2025. PMID: 40203238
-
Cell-Free Synthetic Biology: Engineering Beyond the Cell.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016 Dec 1;8(12):a023853. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a023853. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2016. PMID: 27742731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methodologies for preparation of prokaryotic extracts for cell-free expression systems.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020 Jul 30;5(4):252-267. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2020.07.006. eCollection 2020 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32775710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quorum Sensing and Metabolic State of the Host Control Lysogeny-Lysis Switch of Bacteriophage T1.mBio. 2019 Sep 10;10(5):e01884-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01884-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31506310 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-Care Analyte Quantification and Digital Readout via Lysate-Based Cell-Free Biosensors Interfaced with Personal Glucose Monitors.ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Nov 19;10(11):2862-2869. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00282. Epub 2021 Oct 21. ACS Synth Biol. 2021. PMID: 34672518 Free PMC article.
-
Automated design of protein-binding riboswitches for sensing human biomarkers in a cell-free expression system.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 27;14(1):2416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38098-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37105971 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophobic mismatch drives self-organization of designer proteins into synthetic membranes.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 11;15(1):3162. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47163-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38605024 Free PMC article.
-
A Design of Experiments Approach for Enhancing Room Temperature Stability of a Lyophilised and Paper-Based Bacterial Cell-Free System.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Feb 22;12(3):223. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12030223. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zubay G (1973) In Vitro Synthesis of Protein in Microbial Systems. Annu. Rev. Genet 7 (1), 267–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

