Chemogenomic model identifies synergistic drug combinations robust to the pathogen microenvironment
- PMID: 30596642
- PMCID: PMC6329523
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006677
Chemogenomic model identifies synergistic drug combinations robust to the pathogen microenvironment
Abstract
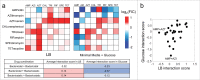
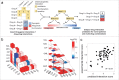
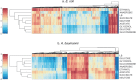
Antibiotics need to be effective in diverse environments in vivo. However, the pathogen microenvironment can have a significant impact on antibiotic potency. Further, antibiotics are increasingly used in combinations to combat resistance, yet, the effect of microenvironments on drug-combination efficacy is unknown. To exhaustively explore the impact of diverse microenvironments on drug-combinations, here we develop a computational framework-Metabolism And GENomics-based Tailoring of Antibiotic regimens (MAGENTA). MAGENTA uses chemogenomic profiles of individual drugs and metabolic perturbations to predict synergistic or antagonistic drug-interactions in different microenvironments. We uncovered antibiotic combinations with robust synergy across nine distinct environments against both E. coli and A. baumannii by searching through 2556 drug-combinations of 72 drugs. MAGENTA also accurately predicted the change in efficacy of bacteriostatic and bactericidal drug-combinations during growth in glycerol media, which we confirmed experimentally in both microbes. Our approach identified genes in glycolysis and glyoxylate pathway as top predictors of synergy and antagonism respectively. Our systems approach enables tailoring of antibiotic therapies based on the pathogen microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

