Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) evaluation of tulathromycin against Haemophilus parasuis in an experimental neutropenic guinea pig model
- PMID: 30596709
- PMCID: PMC6312216
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209177
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) evaluation of tulathromycin against Haemophilus parasuis in an experimental neutropenic guinea pig model
Abstract
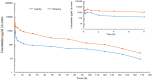
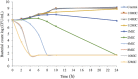
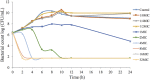
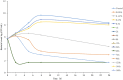
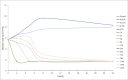
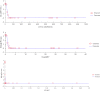
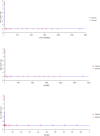
The objective of the study was to develop an ex-vivo PK/PD model of intramuscular (IM) administration of tulathromycin and to test its efficacy against Haemophilus parasuis (H. parasuis) infection in intraperitoneal-inoculated neutropenic guinea pigs. The pharmacokinetics (PKs) of tulathromycin at doses of 1 and 10 mg/kg in H. parasuis-infected neutropenic guinea pig were studied by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). In vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), mutant prevention concentration (MPC), post-antibiotic effect (PAE) and dynamic time-kill curve experiments were carried out using H. parasuis strain 13R. Tulathromycin exhibited concentration-dependent activity and PAE persisted long after administration of the antibiotic. The ratio of the 24-h area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) to MIC in serum (AUC24h/MICserum) was recognized as an important PK/PD parameter that positively correlated with the in vitro antibacterial effectiveness of tulathromycin (R2 = 0.9961 or R2 = 1). For the 1 and 10 mg/kg treatments with tulathromycin, the values of AUC24h/MIC for H. parasuis bacteriostatic action, bactericidal action and virtual bacterial eradication were respectively 22.73, 34.5 and 88.03 h for the 1 mg/kg treatment and respectively 24.94, 30.94 and 49.92 h for the 10 mg/kg treatment. In addition, we demonstrated that doses of 7.2-8.0 mg/kg of tulathromycin resulted in high eradication rates (99.99%). Using a previously published conversion factor of 0.296, we were able to estimate an approximate dose, 2.1-2.4 mg/kg, that should also obtain high eradication rates in the target animal, pigs. This study can help optimize tulathromycin efficacy against H. parasuis infections in swine farming.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Lili Guo is employed by Qingdao Yebio Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Morselt M. [Tulathromycin, a new antibiotic for farm animals]. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 2004;129(9):306–7. . - PubMed
-
- Evans NA. Tulathromycin: Overview of a new triamilide antimicrobial for the treatment of respiratory diseases in cows and pigs. Tieraerztl Umschau. 2006;61(5):A1–A8. WOS:000237369100008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

