Characterization of inflammatory response in hepatorenal syndrome: Relationship with kidney outcome and survival
- PMID: 30597709
- PMCID: PMC6767546
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.14037
Characterization of inflammatory response in hepatorenal syndrome: Relationship with kidney outcome and survival
Abstract
Background: Several lines of evidence indicate that decompensated cirrhosis is characterized by the presence of systemic inflammation. Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS-AKI) is a unique type of renal failure that occurs at late stages of cirrhosis. However, confirmation of the presence and significance of such inflammatory response in HRS-AKI is lacking.
Aim and methods: To characterize the systemic inflammatory response, as estimated by measuring a large number of cytokines, in 161 patients hospitalized for an acute decompensation of cirrhosis: 44 patients without acute kidney injury (AKI), 63 patients with hypovolaemia-induced AKI and 58 patients with HRS-AKI.
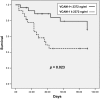
Results: HRS-AKI was characterized by an altered cytokine profile compared to the other two groups, particularly IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, VCAM-1, fractalkine and MIP-1α. The inflammatory response was not related to presence of bacterial infection, concomitant acute-on-chronic liver failure or severity of renal dysfunction. Patients who responded to terlipressin and albumin had only a decrease in TNF-α and RANTES after treatment without changes in other cytokines. Interestingly, patients with persistent HRS-AKI had higher levels of IP-10 and VCAM-1 compared to those with resolution of HRS-AKI. VCAM-1 was also an independent predictor of 3-month mortality. A systems biology analysis approach showed that the inflammatory status of HRS-AKI was similar to that of chronic nonhepatic inflammatory conditions, such as lupus erythematosus or inflammatory bowel disease.
Conclusion: Hepatorenal syndrome is characterized by a marked systemic inflammatory state, reminiscent of that of nonhepatic inflammatory diseases, that correlates with patient outcomes.
Keywords: AKI; cirrhosis; hepatorenal syndrome; inflammation.
© 2018 The Authors. Liver International Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
PG reports Investigator Research grant and Advisory Board work from Grifols, Investigator Research grant and Advisory Board from Gilead, Investigator Research grant from Mallinckrodt, Advisory Board for Promethera, Advisory Board for Martin‐Pharmaceuticals, grants from Ferring‐Pharmaceuticals, grants and Advisory Board Work from Sequana, outside the submitted work. No other authors have any declared interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Systemic inflammation in hepatorenal syndrome - A target for novel treatment strategies?Liver Int. 2019 Jul;39(7):1199-1201. doi: 10.1111/liv.14057. Liver Int. 2019. PMID: 31290276 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

