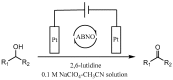
Electrochemical Performance of ABNO for Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols in Acetonitrile Solution
- PMID: 30597882
- PMCID: PMC6337132
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24010100
Electrochemical Performance of ABNO for Oxidation of Secondary Alcohols in Acetonitrile Solution
Abstract
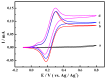
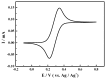
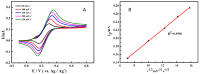
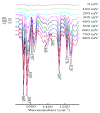
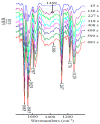
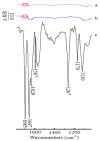
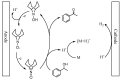
The ketones was successfully prepared from secondary alcohols using 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane-N-oxyl (ABNO) as the catalyst and 2,6-lutidine as the base in acetonitrile solution. The electrochemical activity of ABNO for oxidation of 1-phenylethanol was investigated by cyclic voltammetry, in situ Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and constant current electrolysis experiments. The resulting cyclic voltammetry indicated that ABNO exhibited much higher electrochemical activity when compared with 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) under the similar conditions. A reasonable reaction mechanism of the electrocatalytic oxidation of 1-phenylethanol to acetophenone was proposed. In addition, a series of secondary alcohols could be converted to the corresponding ketones at room temperature in 80⁻95% isolated yields.
Keywords: ABNO; electrochemical; in situ FTIR; ketones; secondary alcohols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhan B.Z., Thompson A. Recent developments in the aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Tetrahedron. 2004;60:2917–2935. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2004.01.043. - DOI
-
- Demizu Y., Shiigi H., Oda T., Matsumura Y., Onomura O. Efficient oxidation of alcohols electrochemically mediated by azabicyclo-N-oxyls. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008;49:48–52. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.11.016. - DOI
-
- Sheldon R.A., Arends I.W.C.E., Dijksman A. New developments in catalytic alcohol oxidations for fine chemicals synthesis. Catal. Today. 2000;57:157–166. doi: 10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00317-X. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

