Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer
- PMID: 30597890
- PMCID: PMC6357121
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11010030
Effects of Antiangiogenetic Drugs on Microcirculation and Macrocirculation in Patients with Advanced-Stage Renal Cancer
Abstract
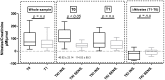
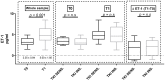
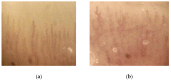
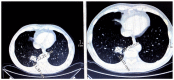
Adverse cardiovascular effects, including hypertension, were described in patients with different cancers treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). The mechanism of TKI-related hypertension is still debated. The aim of this work was to study the effects of TKI on blood pressure (BP), searching for a relationship with possible causative factors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. We included 29 patients in a prospective, observational study; 22 were treated with a first-line drug (sunitinib), while seven participated in the second-line treatment (axitinib or cabozantinib). Patients were investigated at the beginning of antiangiogenic therapy (T0) and at one (T1), three (T2), and six months (T3) after treatment. Patients were evaluated by office blood pressure (BP) and ultrasonography to measure flow-mediated dilatation (FMD), and carotid artery distensibility (cDC) by echocardiography and nailfold capillaroscopy. Plasma endothelin-1 (p-ET-1), urine nitrates, and proteins were also measured. At T1, systolic BP, along with U proteins and p-ET-1, increased significantly. In patients with a clinically significant increase in BP (defined as either the need for an antihypertensive drug or systolic blood pressure (SBP) T1⁻T0 ≥10 and/or SBP ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) T1⁻T0 ≥5 and/or DBP ≥90 mmHg), the urine nitrate concentration was lower at T0, whereas there were no differences in the p-ET-1 and U proteins. Seventeen participants showed changes in the capillaroscopic pattern at T1 with no association with BP increases. There were no differences in the FMD, cDC, and echocardiographic parameters. Our findings are consistent with those of previous studies about BP increases by TKI, and suggest a role of nitric oxide in BP maintenance in this population.
Keywords: NO (Nitric Oxide); TKI; VEGF; angiogenesis; capillaroscopy; endothelin-1; hypertension; renal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to declare; in particular any financial support or other benefits from commercial sources for the work reported on in the manuscript, or any other financial interests that any of the authors may have, which could create a potential conflict of interest or the appearance of a conflict of interest with regard to the work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microvascular Structural Alterations in Cancer Patients Treated With Antiangiogenic Drugs.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 10;8:651594. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.651594. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33778028 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in Blood Pressure Associated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Targeting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.JACC CardioOncol. 2019 Sep 24;1(1):24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2019.08.012. eCollection 2019 Sep. JACC CardioOncol. 2019. PMID: 34396159 Free PMC article.
-
2019 Consensus Statement of the Taiwan Hypertension Society and the Taiwan Society of Cardiology on Renal Denervation for the Management of Arterial Hypertension.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019 May;35(3):199-230. doi: 10.6515/ACS.201905_35(3).20190415A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2019. PMID: 31249454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluid status, blood pressure, and cardiovascular abnormalities in patients on peritoneal dialysis.Perit Dial Int. 2002 Jul-Aug;22(4):477-87. Perit Dial Int. 2002. PMID: 12322819 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of Hypertension: Which Goal for Which Patient?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:117-127. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_97. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27722961 Review.
Cited by
-
Microvascular Structural Alterations in Cancer Patients Treated With Antiangiogenic Drugs.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 10;8:651594. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.651594. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33778028 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Tumor Mutation Burden Related lncRNA Signature Identified Prognosis and Tumor Immune Microenvironment Features in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(8):1503-1518. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220926123923. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 36165528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamnvik O.P., Choueiri T.K., Turchin A., McKay R.R., Goyal L., Davis M., Kaymakcalan M.D., Williams J.S. Clinical risk factors for the development of hypertension in patients treated with inhibitors of the VEGF signaling pathway. Cancer. 2015;121:311–319. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28972. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

