Adsorption Analyses of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions Using Magadiite Modified with Organo-Functional Groups: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies
- PMID: 30597910
- PMCID: PMC6337348
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12010096
Adsorption Analyses of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions Using Magadiite Modified with Organo-Functional Groups: Kinetic and Equilibrium Studies
Abstract
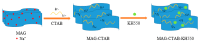
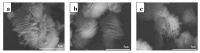
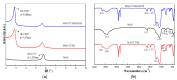
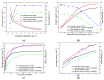
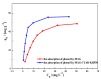
Organically-modified magadiite (MAG⁻CTAB⁻KH550) was synthesized via ion-exchange method and condensation reaction in the presence of pure magadiite (MAG), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (KH550) in aqueous solution in this research. This new adsorbent material was studied using scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and N₂ adsorption/desorption isotherms process. It was found that the MAG⁻CTAB⁻KH550 has high Brunaur-Emmet-Teller (BET) specific surface area and mesoporous pore size distribution which enhanced its ability to remove phenol in aqueous solution; and, the value of pH has a relatively large impact on the adsorption behavior of the sorbent. Finally, the adsorptive behavior of the mesoporous material on phenol was followed pseudo-second-order kinetic adsorption model. In contrast, the adsorption equilibrium isotherm was better performed Langmuir isotherm model than the Freundlich isotherm model; in addition, the results also showed that the MAG⁻CTAB⁻KH550 had a better adsorption capacity and removal efficiency than MAG.
Keywords: adsorption; adsorption isotherms; adsorption kinetics; magadiite; phenol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preparation and Characterization of Magadiite⁻Magnetite Nanocomposite with Its Sorption Performance Analyses on Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Apr 2;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/polym11040607. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30960591 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto organomodified Tirebolu bentonite: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study.J Hazard Mater. 2009 Dec 15;172(1):353-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.019. Epub 2009 Jul 14. J Hazard Mater. 2009. PMID: 19656623
-
Chitosan/MCM-48 nanocomposite as a potential adsorbent for removing phenol from aqueous solution.RSC Adv. 2020 Jun 19;10(39):23417-23430. doi: 10.1039/d0ra02960b. eCollection 2020 Jun 16. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35520349 Free PMC article.
-
Novel eco-friendly amino-modified nanoparticles for phenol removal from aqueous solution.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Aug;27(24):30694-30705. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09313-y. Epub 2020 May 29. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32468377
-
Progress in Development of Magadiite to Produce Multifunctional Lamellar Materials.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023 Sep 20;15(37):43234-43250. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c15785. Epub 2022 Jan 3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 34978785 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising Low-Cost Adsorbent from Waste Green Tea Leaves for Phenol Removal in Aqueous Solution.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 24;19(11):6396. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116396. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35681981 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of phenol from wastewater using Luffa cylindrica fibers in a packed bed column: Optimization, isotherm and kinetic studies.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 17;10(4):e26443. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26443. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38420395 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Characterization of Magadiite⁻Magnetite Nanocomposite with Its Sorption Performance Analyses on Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Apr 2;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/polym11040607. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30960591 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Dynamic Mechanical Properties of XNBR Using ILs/KH550-Functionalized Multilayer Graphene.Materials (Basel). 2019 Aug 30;12(17):2800. doi: 10.3390/ma12172800. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480334 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic Liquid Agar-Alginate Beads as a Sustainable Phenol Adsorbent.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 28;14(5):984. doi: 10.3390/polym14050984. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Moraes M.F., de Oliveira T.F., Cuellar J., Castiglioni G.L. Phenol degradation using adsorption methods, advanced oxidative process (H2O2/UV) and H2O2/UV/activated carbon coupling: influence of homogeneous and heterogeneous phase. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017;100:38–45. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2017.21808. - DOI
-
- Khardenacis A.A., Kapley A., Purohit H.J. Phenol-mediated improved performance of active biomass for treatment of distillery wastewater. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2008;62:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2007.06.016. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

