Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders
- PMID: 30597930
- PMCID: PMC6359056
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11010008
Intranasal Delivery of Genistein-Loaded Nanoparticles as a Potential Preventive System against Neurodegenerative Disorders
Abstract
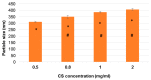
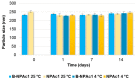
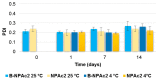
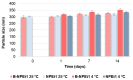
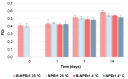
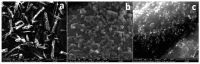
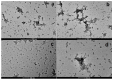
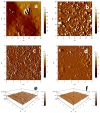
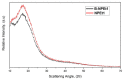
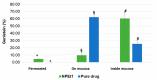
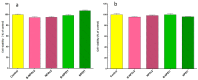
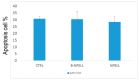
Genistein has been reported to have antioxidant and neuroprotective activity. Despite encouraging in vitro and in vivo results, several disadvantages such as poor water solubility, rapid metabolism, and low oral bioavailability limit the clinical application of genistein. The aim of this study was to design and characterize genistein-loaded chitosan nanoparticles for intranasal drug delivery, prepared by the ionic gelation technique by using sodium hexametaphosphate. Nanoparticles were characterized in vitro and their cytotoxicity was tested on PC12 cells. Genistein-loaded nanoparticles were prepared, and sodium hexametaphosphate was used as a valid alternative to well-known cross-linkers. Nanoparticle characteristics as well as their physical stability were affected by formulation composition and manufacturing. Small (mean diameters of 200⁻300 nm) and homogeneous nanoparticles were obtained and were able to improve genistein penetration through the nasal mucosa as compared to pure genistein. Nanoparticle dispersions showed a pH consistent with the nasal fluid and preserved PC12 cell vitality.
Keywords: chitosan; genistein; intranasal delivery; nanoparticles; neurodegenerative disease; nose-to-brain; sodium hexametaphosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The nasal delivery of nanoencapsulated statins - an approach for brain delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Dec 7;11:6575-6590. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S119033. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27994459 Free PMC article.
-
Nose to Brain Delivery of Galantamine Loaded Nanoparticles: In-vivo Pharmacodynamic and Biochemical Study in Mice.Curr Drug Deliv. 2019;16(1):51-58. doi: 10.2174/1567201815666181004094707. Curr Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30289074
-
Increasing protective activity of genistein by loading into transfersomes: A new potential adjuvant in the oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative diseases?Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.207. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30599903
-
Lipid Nanoparticles for Nasal/Intranasal Drug Delivery.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2017;34(3):257-282. doi: 10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2017018693. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2017. PMID: 28845761 Review.
-
Chitosan Nanoparticles for Intranasal Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 31;16(6):746. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060746. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Essential Oil-Loaded NLC for Potential Intranasal Administration.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 28;13(8):1166. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081166. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34452126 Free PMC article.
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Formulative Strategy to Increase Oral Permeation of a Molecule Active in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Management.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 24;12(12):1132. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121132. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33255304 Free PMC article.
-
Particles Containing Cells as a Strategy to Promote Remyelination in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurol. 2020 Jul 7;11:638. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00638. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32733364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rose Bengal-Chitosan Nanocomposites for Oral Administration.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025 May 8;15(10):706. doi: 10.3390/nano15100706. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40423096 Free PMC article.
-
Ionotropic Gelation-Based Synthesis of Chitosan-Metal Hybrid Nanoparticles Showing Combined Antimicrobial and Tissue Regenerative Activities.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Nov 12;13(22):3910. doi: 10.3390/polym13223910. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833209 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

