Efficient Synthesis of PVDF/PI Side-by-Side Bicomponent Nanofiber Membrane with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Good Thermal Stability
- PMID: 30597932
- PMCID: PMC6359095
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9010039
Efficient Synthesis of PVDF/PI Side-by-Side Bicomponent Nanofiber Membrane with Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Good Thermal Stability
Abstract
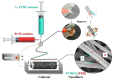
Bicomponent composite fibers, due to their unique versatility, have attracted great attention in many fields, such as filtration, energy, and bioengineering. Herein, we efficiently fabricated polyvinylidene fluoride/polyimide (PVDF/PI) side-by-side bicomponent nanofibers based on electrospinning, which resulted in the synergism between PVDF and PI, and eventually obtained the effect of 1 + 1 > 2. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were used to characterize the morphology and chemical structure of nanofibers, indicating that a large number of side-by-side nanofibers were successfully prepared. Further, the thermal stability, mechanical strength, and filtration properties of PVDF/PI were carefully investigated. The results revealed that the bicomponent nanofibers possessed both good mechanical strength and remarkable thermal stability. Moreover, the mechanical properties of PVDF/ PI were strengthened by more than twice after the heat treatment (7.28 MPa at 25 °C, 15.49 MPa at 230 °C). Simultaneously, after the heat treatment at 230 °C for 30 min, the filtration efficiency of PVDF/PI membrane was maintained at about 95.45 ± 1.09%, and the pressure drop was relatively low. Therefore, the prepared PVDF/PI side-by-side bicomponent nanofibers have a favorable prospect of application in the field of medium- and high-temperature filtration, which further expands the application range of electrospun fiber membranes.
Keywords: PVDF/PI; bicomponent electrospinning; nanofiber; side-by-side.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; and in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Jiang S.H., Chen Y.M., Duan G.G., Mei C.T., Greiner A., Agarwal S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018;9:2685–2720. doi: 10.1039/C8PY00378E. - DOI
-
- He Y.X., Yang S., Liu H., Shao Q., Chen Q.Y., Lu C., Jiang Y.L., Liu C.T., Guo Z.H. Reinforced carbon fiber laminates with oriented carbon nanotube epoxy nanocomposites: Magnetic field assisted alignment and cryogenic temperature mechanical properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;517:40–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.087. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayad E., Cayla A., Rault F., Gonthier A., LeBlan T., Campagne C., Devaux E. Influence of rheological and thermal properties of polymers during melt spinning on bicomponent fiber morphology. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016;25:3296–3302. doi: 10.1007/s11665-016-2193-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

