Improved Preventive Effects of Combined Bioactive Compounds Present in Different Blueberry Varieties as Compared to Single Phytochemicals
- PMID: 30597948
- PMCID: PMC6356906
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11010061
Improved Preventive Effects of Combined Bioactive Compounds Present in Different Blueberry Varieties as Compared to Single Phytochemicals
Abstract
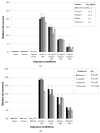
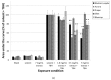
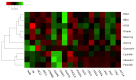
Blueberries contain many different phytochemicals which might be responsible for their disease preventive properties. In a previously conducted human dietary intervention study, we showed that a 4-week intervention with blueberry⁻apple juice protected the participants against oxidative stress and modulated expression of genes involved in different genetic pathways contributing to the antioxidant response. The present study investigates the effect of different blueberry varieties (Elliot, Draper, Bluecrop, and Aurora, and the blueberry⁻apple juice from our previous human dietary intervention study), and four different single compounds (vitamin C, peonidin, cyanidin, and quercetin) on antioxidant capacity and gene expression changes in colonic cells in vitro, and compares the outcome with the earlier in vivo findings. The results demonstrate that all blueberry varieties as well as the blueberry⁻apple juice were more effective in reducing oxidative stress as compared to the single compounds (e.g., DNA strand break reduction: EC50: Elliot 8.3 mg/mL, Aurora and Draper 11.9 mg/mL, blueberry⁻apple juice 12.3 mg/mL, and Bluecrop 12.7 mg/mL; single compounds). In addition, the gene expression profiles (consisting of 18 selected genes from the in vivo study) induced by the blueberry varieties were more similar to the profile of the human intervention study (range 44⁻78%). The blueberry variety Elliot showed the strongest and most similar effects, almost 80% of gene expression modulations were similar compared to the in vivo results. From the single compounds (range 17⁻44%), quercetin induced the most comparable gene expression changes, i.e., 44%. This approach could be useful in agriculture for identifying crop varieties containing combinations of phytochemicals which show optimal preventive capacities.
Keywords: (combinations of) phytochemicals; antioxidant capacity; blueberry extracts; disease risk reduction; gene expression profiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Cancer Research Fund. American Institute for Cancer Research . Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective. American Institute for Cancer Research; Washington, DC, USA: 2007. p. 517.
-
- Kok T.M., Breda S.G., Briede J.J. Genomics-based identification of molecular mechanisms behind the cancer preventive action of phytochemicals: Potential and challenges. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012;13:255–264. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

