A New Class of Synthetic Flavonolignan-Like Dimers: Still Few Molecules, but with Attractive Properties
- PMID: 30597952
- PMCID: PMC6337569
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24010108
A New Class of Synthetic Flavonolignan-Like Dimers: Still Few Molecules, but with Attractive Properties
Abstract
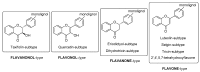
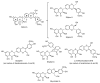
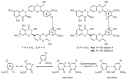
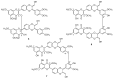
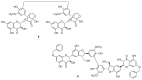
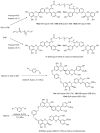
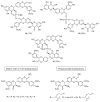
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in dimeric molecules due to reports of their promising therapeutic value in the treatment of numerous diseases (such as cancer, HIV, Alzheimer's and, malaria). Many reports in the literature have highlighted the ability of these molecules to interact not only with specific biologic receptors but also to induce a biological response that more than doubles the results of the corresponding monomeric counterpart. In this regard, flavonolignan dimers or simply bi-flavonolignans are an emerging class of dimeric compounds that unlike bi-flavonoids, which are very widespread in nature, consist of synthetic dimers of some flavonolignans isolated from the milk thistle Silybum marianum [L. Gaertn. (Asteraceae)]. This mini-review will discuss recent developments in the synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of new families of flavonolignan dimers, in light of emerging medicinal chemistry strategies.
Keywords: Silybum marianum; flavonolignans; milk thistle; silibinin; silybin; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Pelter A., Haensel R. The structure of silybin (Silybum substance E6), the first flavonolignan. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968;25:2911–2916. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)89610-0. - DOI
-
- Della Greca M., Mancino A., Previtera L., Zarrelli A., Zuppolini S. Lignans from Phillyrea angustifolia L. Phytochem. Lett. 2011;4:118–121. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2010.12.006. - DOI
-
- Fiorentino A., DellaGreca M., D’Abrosca B., Oriano P., Golino A., Izzo A., Zarrelli A., Monaco P. Lignans, neolignans and sesquilignans from Cestrum parqui l’Her. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007;35:392–396. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2006.12.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

