Drug-Loaded Biocompatible Nanocarriers Embedded in Poloxamer 407 Hydrogels as Therapeutic Formulations
- PMID: 30597953
- PMCID: PMC6473859
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines6010007
Drug-Loaded Biocompatible Nanocarriers Embedded in Poloxamer 407 Hydrogels as Therapeutic Formulations
Abstract
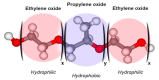
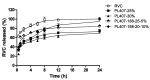
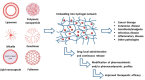
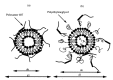
Hydrogels are three-dimensional networks of hydrophilic polymers able to absorb and retain a considerable amount of water or biological fluid while maintaining their structure. Among these, thermo-sensitive hydrogels, characterized by a temperature-dependent sol⁻gel transition, have been massively used as drug delivery systems for the controlled release of various bioactives. Poloxamer 407 (P407) is an ABA-type triblock copolymer with a center block of hydrophobic polypropylene oxide (PPO) between two hydrophilic polyethyleneoxide (PEO) lateral chains. Due to its unique thermo-reversible gelation properties, P407 has been widely investigated as a temperature-responsive material. The gelation phenomenon of P407 aqueous solutions is reversible and characterized by a sol⁻gel transition temperature. The nanoencapsulation of drugs within biocompatible delivery systems dispersed in P407 hydrogels is a strategy used to increase the local residence time of various bioactives at the injection site. In this mini-review, the state of the art of the most important mixed systems made up of colloidal carriers localized within a P407 hydrogel will be provided in order to illustrate the possibility of obtaining a controlled release of the entrapped drugs and an increase in their therapeutic efficacy as a function of the biomaterial used.
Keywords: colloids; controlled drug release; ethosomes; liposomes; nanoparticles; niosomes; poloxamer 407.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Pitorre M., Gondé H., Haury C., Messous M., Poilane J., Boudaud D., Kanber E., Rossemond Ndombina G.A., Benoit J.P., Bastiat G. Recent advances in nanocarrier-loaded gels: Which drug delivery technologies against which diseases? J. Control. Release. 2017;266:140–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.09.031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

