NAP Family CG5017 Chaperone Pleiotropically Regulates Human AHR Target Genes Expression in Drosophila Testis
- PMID: 30597983
- PMCID: PMC6337364
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20010118
NAP Family CG5017 Chaperone Pleiotropically Regulates Human AHR Target Genes Expression in Drosophila Testis
Abstract
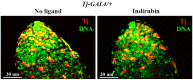
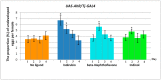
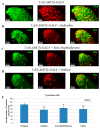
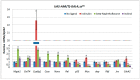
To study the regulatory mechanism of the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), target genes of transcription are necessary for understanding the normal developmental and pathological processes. Here, we examined the effects of human AHR ligands on male fecundity. To induce ectopic human AhR gene expression, we used Drosophila melanogaster transformed with human AhR under the control of a yeast UAS promoter element capable of activation in the two-component UAS-GAL4 system. We found that exogenous AHR ligands decrease the number of Drosophila gonadal Tj-positive cells. We also found both an increase and decrease of AHR target gene expression, including in genes that control homeostasis and testis development. This suggests that gonadal AHR activation may affect the expression of gene networks that control sperm production and could be critical for fertility not just in Drosophila but also in humans. Finally, we found that the activation of the expression for some AHR target genes depends on the expression of testis-specific chaperone CG5017 in gonadal cells. Since CG5017 belongs to the nucleosome assembly protein (NAP) family and may participate in epigenetic regulation, we propose that this nucleotropic chaperone is essential to provide the human AHR with access to only the defined set of its target genes during spermatogenesis.
Keywords: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; CG5017; Drosophila; nucleosome assembly protein; spermatogenesis; xenobiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Israel D.I., Whitlock J.P. Regulation of cytochrome P1–450 gene transcription by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259:5400–5402. - PubMed
-
- Emmons R.B., Duncan D., Estes P.A., Kiefel P., Mosher J.T., Sonnenfeld M., Ward M.P., Duncan I., Crews S.T. The spineless-aristapedia and tango bHLH-PAS proteins interact to control antennal and tarsal development in Drosophila. Development. 1999;126:3937–3945. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

