Revealing transcription factor and histone modification co-localization and dynamics across cell lines by integrating ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data
- PMID: 30598100
- PMCID: PMC6311957
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-5278-5
Revealing transcription factor and histone modification co-localization and dynamics across cell lines by integrating ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data
Abstract
Background: Interactions among transcription factors (TFs) and histone modifications (HMs) play an important role in the precise regulation of gene expression. The context specificity of those interactions and further its dynamics in normal and disease remains largely unknown. Recent development in genomics technology enables transcription profiling by RNA-seq and protein's binding profiling by ChIP-seq. Integrative analysis of the two types of data allows us to investigate TFs and HMs interactions both from the genome co-localization and downstream target gene expression.
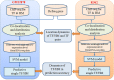
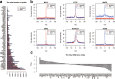
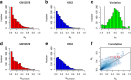
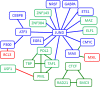
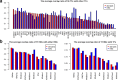
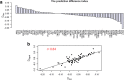
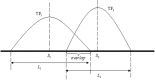
Results: We propose a integrative pipeline to explore the co-localization of 55 TFs and 11 HMs and its dynamics in human GM12878 and K562 by matched ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data from ENCODE. We classify TFs and HMs into three types based on their binding enrichment around transcription start site (TSS). Then a set of statistical indexes are proposed to characterize the TF-TF and TF-HM co-localizations. We found that Rad21, SMC3, and CTCF co-localized across five cell lines. High resolution Hi-C data in GM12878 shows that they associate most of the Hi-C peak loci with a specific CTCF-motif "anchor" and supports that CTCF, SMC3, and RAD2 co-localization serves important role in 3D chromatin structure. Meanwhile, 17 TF-TF pairs are highly dynamic between GM12878 and K562. We then build SVM models to correlate high and low expression level of target genes with TF binding and HM strength. We found that H3k9ac, H3k27ac, and three TFs (ELF1, TAF1, and POL2) are predictive with the accuracy about 85~92%.
Conclusion: We propose a pipeline to analyze the co-localization of TF and HM and their dynamics across cell lines from ChIP-seq, and investigate their regulatory potency by RNA-seq. The integrative analysis of two level data reveals new insight for the cooperation of TFs and HMs and is helpful in understanding cell line specificity of TF/HM interactions.
Keywords: Co-localization; Dynamics; Histone modification; Transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of ChIP-seq in the discovery of transcription factor binding sites, differential gene regulation mechanism, epigenetic marks and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2847-52. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949201. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between histone modifications and transcription factor binding is protein family specific.Genome Res. 2018 Mar 1;28(3):321-333. doi: 10.1101/gr.220079.116. Genome Res. 2018. PMID: 29326300 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative binding of transcription factors in the human genome.Genomics. 2020 Sep;112(5):3427-3434. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.06.029. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32574834
-
7C: Computational Chromosome Conformation Capture by Correlation of ChIP-seq at CTCF motifs.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 25;20(1):777. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6088-0. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31653198 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating ChIP-seq with other functional genomics data.Brief Funct Genomics. 2018 Mar 1;17(2):104-115. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely002. Brief Funct Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29579165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated multiomics analysis of chromosome 19 miRNA cluster in bladder cancer.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Aug 5;23(3):266. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01191-0. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37542643 Free PMC article.
-
PIBF1 regulates multiple gene expression via impeding long-range chromatin interaction to drive the malignant transformation of HPV16 integration epithelial cells.J Adv Res. 2024 Mar;57:163-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.04.015. Epub 2023 May 13. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37182685 Free PMC article.
-
3Scover: Identifying Safeguard TF from Cell Type-TF Specificity Network by an Extended Minimum Set Cover Model.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101227. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101227. Epub 2020 Jun 2. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32554189 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric Predictive Relationships Across Histone Modifications.Nat Mach Intell. 2022 Mar;4(3):288-299. doi: 10.1038/s42256-022-00455-x. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Nat Mach Intell. 2022. PMID: 35529103 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting CTCF cell type active binding sites in human genome.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82238-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738353 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

