An upstream enhancer regulates Gpihbp1 expression in a tissue-specific manner
- PMID: 30598475
- PMCID: PMC6446700
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M091322
An upstream enhancer regulates Gpihbp1 expression in a tissue-specific manner
Abstract
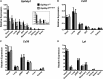
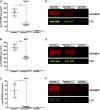
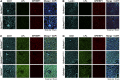
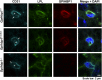
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1), the protein that shuttles LPL to the capillary lumen, is essential for plasma triglyceride metabolism. When GPIHBP1 is absent, LPL remains stranded within the interstitial spaces and plasma triglyceride hydrolysis is impaired, resulting in severe hypertriglyceridemia. While the functions of GPIHBP1 in intravascular lipolysis are reasonably well understood, no one has yet identified DNA sequences regulating GPIHBP1 expression. In the current studies, we identified an enhancer element located ∼3.6 kb upstream from exon 1 of mouse Gpihbp1. To examine the importance of the enhancer, we used CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to create mice lacking the enhancer (Gpihbp1Enh/Enh). Removing the enhancer reduced Gpihbp1 expression by >90% in the liver and by ∼50% in heart and brown adipose tissue. The reduced expression of GPIHBP1 was insufficient to prevent LPL from reaching the capillary lumen, and it did not lead to hypertriglyceridemia-even when mice were fed a high-fat diet. Compound heterozygotes (Gpihbp1Enh/- mice) displayed further reductions in Gpihbp1 expression and exhibited partial mislocalization of LPL (increased amounts of LPL within the interstitial spaces of the heart), but the plasma triglyceride levels were not perturbed. The enhancer element that we identified represents the first insight into DNA sequences controlling Gpihbp1 expression.
Keywords: chylomicrons; endothelial cells; fatty acid metabolism; glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein–binding protein 1; lipids; lipolysis; triglycerides.
Copyright © 2019 Allan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interests to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Goldberg I. J. 1996. Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: Central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. J. Lipid Res. 37: 693–707. - PubMed
-
- Kristensen K. K., Midtgaard S. R., Mysling S., Kovrov O., Hansen L. B., Skar-Gislinge N., Beigneux A. P., Kragelund B. B., Olivecrona G., Young S. G., et al. . 2018. A disordered acidic domain in GPIHBP1 harboring a sulfated tyrosine regulates lipoprotein lipase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 115: E6020–E6029. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL087228/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES006694/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM065490/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL140198/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125335/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL090553/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL139725/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007895/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL123485/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL123485/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL146358/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

