A taxonomic revision and molecular phylogeny of the eastern Palearctic species of the genera Schizomyia Kieffer and Asteralobia Kovalev (Diptera, Cecidomyiidae, Asphondyliini), with descriptions of five new species of Schizomyia from Japan
- PMID: 30598610
- PMCID: PMC6305770
- DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.808.29679
A taxonomic revision and molecular phylogeny of the eastern Palearctic species of the genera Schizomyia Kieffer and Asteralobia Kovalev (Diptera, Cecidomyiidae, Asphondyliini), with descriptions of five new species of Schizomyia from Japan
Abstract
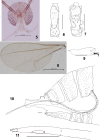
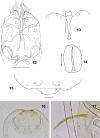
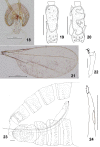
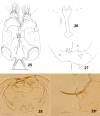
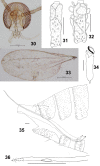
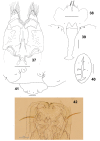
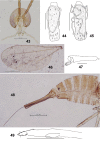
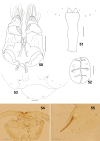
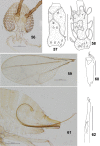
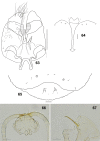
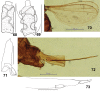
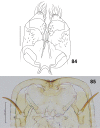
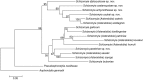
The genus Asteralobia (Diptera, Cecidomyiidae, Asphondyliini, Schizomyiina) was erected by Kovalev (1964) based on the presence of constrictions on the cylindrical male flagellomeres. In the present study, we examine the morphological features of Asteralobia and Schizomyia and found that the male flagellomeres are constricted also in Schizomyiagaliorum, the type species of Schizomyia. Because no further characters clearly separating Asteralobia from Schizomyia were observed, we synonymize Asteralobia under Schizomyia. Molecular phylogenetic analysis strongly supports our taxonomic treatment. We describe five new species of Schizomyia from Japan, S.achyranthesae Elsayed & Tokuda, sp. n., S.diplocyclosae Elsayed & Tokuda, sp. n., S.castanopsisae Elsayed & Tokuda, sp. n., S.usubai Elsayed & Tokuda, sp. n., and S.paederiae Elsayed & Tokuda, sp. n., and redescribe three species, S.galiorum Kieffer, S.patriniae Shinji, and S.asteris Kovalev. A taxonomic key to the Japanese Schizomyia species is provided.
Keywords: Cecidomyiinae; Schizomyiina; gall midges; taxonomic key.
Figures





References
-
- Elsayed AK, Ogata K, Kaburagi K, Yukawa J, Tokuda M. (2017) A new Dasineura species (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) associated with Symplocoscochinchinensis (Loureiro) (Symplocaceae) in Japan. Japanese Journal of Systematic Entomology 23: 81–86.
-
- Elsayed AK, Uechi N, Yukawa J, Tokuda M. (in press) Ampelomyia, a new genus of Schizomyiina (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) associated with Vitis (Vitaceae) in the Palaearctic and Nearctic regions, with description of a new species from Japan. The Canadian Entomologist.
-
- Fedotova ZA. (2002) New species of gall midges (Diptera, Cecidomyiidae) from the Russian Far East. Far Eastern Entomologist 118: 1–35.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
