Pemphigus vulgaris - A report of three cases and review of literature
- PMID: 30598970
- PMCID: PMC6259552
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_133_18
Pemphigus vulgaris - A report of three cases and review of literature
Abstract
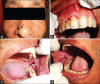
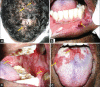
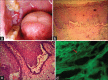
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is an autoimmune, potentially life-threatening disease causing blisters and erosions of the skin and mucous membranes associated with intraepithelial acantholysis. The underlying mechanism responsible for causing intraepithelial lesions is the binding of immunoglobulin G autoantibodies to desmoglein 3, a transmembrane glycoprotein adhesion molecule present on desmosomes. Histological features comprise intraepithelial cleft and Tzanck cells. Corticosteroids remain the mainstay of the treatment plan. In this article, we have discussed about the diagnosis of three patients suffering from PV, the treatment rendered, and the outcome of the same.
Keywords: Corticosteroids; Nikolsky's sign; Tzanck cells; vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nikolsky's sign on the gingival mucosa: a clinical tool for oral health practitioners.J Periodontol. 2008 Dec;79(12):2241-6. doi: 10.1902/jop.2008.080217. J Periodontol. 2008. PMID: 19053912
-
Pemphigus vulgaris: a case report.Pan Afr Med J. 2022 Jul 7;42:184. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2022.42.184.34184. eCollection 2022. Pan Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 36212921 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Desmoglein Antibodies in Patients With Pemphigus Vulgaris.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1190. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01190. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutaneous pemphigus vulgaris with skin features similar to the classic mucocutaneous type: a case report and review of the literature.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008 Nov;33(6):724-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02871.x. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18627395 Review.
-
Serum from pemphigus vulgaris reduces desmoglein 3 half-life and perturbs its de novo assembly to desmosomal sites in cultured keratinocytes.FEBS Lett. 2006 May 29;580(13):3276-81. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.089. Epub 2006 May 8. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16698018
Cited by
-
Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris: A Case Report With Review of Literature.Cureus. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):e48839. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48839. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38106742 Free PMC article.
-
Nikolsky's sign: A pathognomic boon.J Family Med Prim Care. 2020 Feb 28;9(2):526-530. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_889_19. eCollection 2020 Feb. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020. PMID: 32318376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Juvenile pemphigus vulgaris: A narrative review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 23;104(21):e42611. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042611. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40419903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Removable Prosthetic Treatment in Oral Pemphigus Vulgaris: Report of Three Cases.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019 Jun 19;9(4):423-426. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_421_18. eCollection 2019 Jul-Aug. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019. PMID: 31516878 Free PMC article.
-
Oral pemphigus vulgaris diagnostic characteristics and treatment: a systematic review.Med Mol Morphol. 2025 Mar;58(1):1-22. doi: 10.1007/s00795-024-00414-y. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Med Mol Morphol. 2025. PMID: 39680142
References
-
- Lever W. Pemphigus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1953;32:1–123. - PubMed
-
- Rajendran B. Diseases of the skin. In: Shafer WG, Hine MK, Levy BM, editors. Shafer's Textbook of Oral Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Noida; 2012. pp. 825–30.
-
- Pemphigus vulgaris and mucous membrane pemphigoid: Update on etiopathogenesis, oral manifestations and management. J Clin Exp Dent. 2011;3:e246–50.
-
- Seshadri D, Kumaran MS, Kanwar AJ. Acantholysis revisited: Back to basics. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2013;79:120–6. - PubMed

