Long-term Outcomes of Augmentation Cystoplasty in a Pediatric Population With Refractory Bladder Dysfunction: A 12-Year Follow-up Experience at Single Center
- PMID: 30599500
- PMCID: PMC6312970
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.1836174.087
Long-term Outcomes of Augmentation Cystoplasty in a Pediatric Population With Refractory Bladder Dysfunction: A 12-Year Follow-up Experience at Single Center
Abstract
Purpose: Augmentation cystoplasty (AC) is a surgical procedure used in adults and children with refractory bladder dysfunction, including a small bladder capacity and inadequate bladder compliance, and in whom conservative and medical treatment has failed. This study was aimed to determine the long-term outcomes of AC in children.
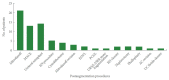
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted of 42 patients (31 males; mean age, 14.2±6.2 years) who underwent AC for neurogenic and nonneurogenic bladder dysfunction, with a median 12.0±1.5 years of follow-up. All patients underwent AC using the ileum with or without continent reconstruction. Pre-AC, concurrent, and post-AC procedures and complications were analyzed. Patients who underwent ureterocystoplasty, were lost to follow-up, or had less than 10 years of follow-up were excluded. The primary outcomes were the complication and continence rates, the post-AC linear rate of height and weight gain, and renal function. The Student t-test was used to evaluate between-group differences and the paired t-test was used to evaluate longitudinal changes in measured variables.
Results: Renal function was stable or improved in 32 of 42 patients (76.2%), with a post-AC continence rate of 88.1%. Thirty patients (71.4%) required 72 procedures post-AC. There was no statistically significant difference in the mean percentile of height (P=0. 212) or weight (P=0.142) of patients in the pre- and post-AC periods. No cases of bladder perforation or malignancy were detected.
Conclusion: We consider AC to be a safe and effective procedure that does not negatively affect future physical growth, while achieving a good rate of stable renal function. Patients need long-term follow-up to address long-term complications.
Keywords: Augmentation cystoplasty; Bladder dysfunction; Physical growth; Urinary bladder calculi.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Does augmentation cystoplasty with continent reconstruction at a young age increase the risk of complications or secondary surgeries?J Pediatr Urol. 2015 Feb;11(1):41.e1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2014.08.016. Epub 2015 Feb 7. J Pediatr Urol. 2015. PMID: 25725612
-
Long-term complications and outcomes of augmentation cystoplasty in children with neurogenic bladder.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 20;14(1):4214. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54431-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38378755 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical outcomes after increasing bladder outlet resistance without augmentation cystoplasty in neurogenic bladder.J Pediatr Urol. 2021 Apr;17(2):235.e1-235.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.11.031. Epub 2020 Nov 28. J Pediatr Urol. 2021. PMID: 33342678
-
Augmentation cystoplasty in the patient with neurogenic bladder.World J Urol. 2020 Dec;38(12):3035-3046. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02919-z. Epub 2019 Sep 11. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31511969 Review.
-
[Lower urinary tract reconstruction by augmentation cystoplasty and insertion of artificial urinary sphincter cuff only: long term follow-up].Prog Urol. 2004 Jun;14(3):310-4. Prog Urol. 2004. PMID: 15373171 Review. French.
Cited by
-
An Acellular Platform to Drive Urinary Bladder Tissue Regeneration.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2025 Jan;8(1):2400158. doi: 10.1002/adtp.202400158. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39822772 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder Augmentation (Enterocystoplasty): the Current State of a Historic Operation.Curr Urol Rep. 2019 Jul 24;20(9):50. doi: 10.1007/s11934-019-0919-z. Curr Urol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31342172 Review.
-
Augmentation Uretero-enterocystoplasty Is an Effective Procedure in Protecting the Upper Urinary Tract Without Accelerating Deterioration of Renal Function.Eur Urol Open Sci. 2023 Mar 31;51:62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2023.03.002. eCollection 2023 May. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2023. PMID: 37187718 Free PMC article.
-
A catheterizable serous-lined urinary outlet associated with the ileal bladder augmentation Abol-Enein and Ghoneim procedure: a safe and reliable procedure in children.Front Pediatr. 2024 Feb 29;12:1273505. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1273505. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38487468 Free PMC article.
-
Augmentation cystoplasty in children with stages III and IV chronic kidney disease secondary to neurogenic bladder.Asian J Urol. 2022 Jul;9(3):313-317. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2021.05.010. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Asian J Urol. 2022. PMID: 36035352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams MC, Joseph DB. Urinary tract reconstruction in children. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. Campbell-Walsh urology. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2007. pp. 3656–702.
-
- Keenan A, Whittam B, Misseri R, Cain M. Long-term outcomes following bladder augmentation in children with neurogenic bladder. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep. 2014;9:275–81.
-
- Surer I, Ferrer FA, Baker LA, Gearhart JP. Continent urinary diversion and the exstrophy-epispadias complex. J Urol. 2003;169:1102–5. - PubMed
-
- Scales CD, Jr, Wiener JS. Evaluating outcomes of enterocystoplasty in patients with spina bifida: a review of the literature. J Urol. 2008;180:2323–9. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi Y, Yamataka A, Kaneyama K, Kato Y, Lane GJ, Miyano T. Review of 86 patients with myelodysplasia and neurogenic bladder who underwent sigmoidocolocystoplasty and were followed more than 10 years. J Urol. 2006;176(4 Pt 2):1806–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

