Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- PMID: 30599506
- PMCID: PMC6344799
- DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2018.12.16
Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
Abstract
As in other domains, artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly important in medicine. In particular,deep learning-based pattern recognition methods can advance the field of pathology byincorporating clinical, radiologic, and genomic data to accurately diagnose diseases and predictpatient prognoses. In this review, we present an overview of artificial intelligence, the brief historyof artificial intelligence in the medical domain, recent advances in artificial intelligence applied topathology, and future prospects of pathology driven by artificial intelligence.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Image analysis; Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
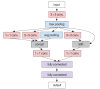

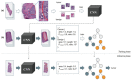
References
-
- McCorduck P. Machines who think: a personal inquiry into the history and prospects of artificial intelligence. Natick: A.K. Peters; 2004.
-
- Turing AM. I. Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind. 1950;59:433–60.
-
- Searle JR. Minds, brains, and programs. Behav Brain Sci. 1980;3:417–24.
-
- Russell SJ, Norvig P. Artificial intelligence: a modern approach. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 2003.
-
- Artificial intelligence [Internet] Wikipedia; 2018. [cited 2018 Dec 9]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_intelligence.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

