Unknown mutations and genotype/phenotype correlations of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in patients from Saudi Arabia and Pakistan
- PMID: 30600594
- PMCID: PMC6418373
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.539
Unknown mutations and genotype/phenotype correlations of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in patients from Saudi Arabia and Pakistan
Abstract
Background: Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) is a genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous skin disease, associated with defects in the skin permeability barrier. Several but not all genes with underlying mutations have been identified, but a clear correlation between genetic causes and clinical picture has not been described to date.
Methods: Our study included 19 families from Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Pakistan. All patients were born to consanguineous parents and diagnosed with ARCI. Mutations were analyzed by homozygosity mapping and direct sequencing.
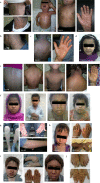
Results: We have detected mutations in all families in five different genes: TGM1, ABCA12, CYP4F22, NIPAL4, and ALOXE3. Five likely pathogenic variants were unknown so far, a splice site and a missense variant in TGM1, a splice site variant in NIPAL4, and missense variants in ABCA12 and CYP4F22. We attributed TGM1 and ABCA12 mutations to the most severe forms of lamellar and erythematous ichthyoses, respectively, regardless of treatment. Other mutations highlighted the presence of a phenotypic spectrum in ARCI.
Conclusion: Our results contribute to expanding the mutational spectrum of ARCI and revealed new insights into genotype/phenotype correlations. The findings are instrumental for a faster and more precise diagnosis, a better understanding of the pathophysiology, and the definition of targets for more specific therapies for ARCI.
Keywords: Skin permeability barrier; congenital ichthyosis; erythema; genotype/phenotype correlation; homozygosity mapping; skin scaling.
© 2019 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflict of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama, M. , Sugiyama‐Nakagiri, Y. , Sakai, K. , McMillan, J. R. , Goto, M. , Arita, K. , … Shimizu, H. (2005). Mutations in lipid transporter ABCA12 in harlequin ichthyosis and functional recovery by corrective gene transfer. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115(7), 1777–1784. 10.1172/jci24834. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Becker, K. , Csikos, M. , Sardy, M. , Szalai, Z. S. , Horvath, A. , & Karpati, S. (2003). Identification of two novel nonsense mutations in the transglutaminase 1 gene in a Hungarian patient with congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. Experimental Dermatology, 12(3), 324–329. 10.1034/j.1600-0625.2003.120313.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

