The Functional Mechanisms of miR-30b-5p in Acute Lung Injury in Children
- PMID: 30600796
- PMCID: PMC6327783
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.911398
The Functional Mechanisms of miR-30b-5p in Acute Lung Injury in Children
Abstract
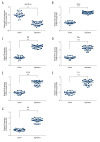
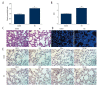
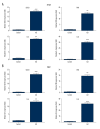
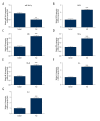
BACKGROUND Acute lung injury in children is a complicated disease linked to the inflammation response. MicroRNA (miRNA) plays a vital role in acute lung injury. However, the role of miR-30b-5p in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury is not clear. The purpose of our study was to investigate the alteration of miR-30b-5p, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3), in children with acute lung injury, and also in a mouse model of acute lung injury induced by the endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS). MATERIAL AND METHODS The levels of miR-30b-5p, SOCS3, FKN (fractalkine), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and IL-8 were detected by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), western blot, and qRT-PCR (quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction) assay. The alveolar permeability index and the ratio of wet weight/dry weight (W/D) were measured. Then, we examined the inflammation and apoptosis using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling) assay. Additionally, SOCS3 was investigated as a direct target of miR-30a-5p in RAW264.7 cells by dual-luciferase reporter assays. RESULTS Our study indicated that the level of miR-30b-5p was decreased and the levels of SOCS3, FKN, TNF-α, NF-κB, IL-6, and IL-8 were increased in lung tissue, serum, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of mice with acute lung injury induced by LPS. In addition, LPS increased alveolar permeability index and the ratio of W/D and induced inflammatory responses, including the activation of the NF-kB pathway in a mouse model. Furthermore, SOCS3 was confirmed to be a target of miR-30a-5p in RAW264.7 cells. CONCLUSIONS Our data demonstrated an important role for miR-30b-5p in acute lung injury inflammation and suggested that miR-30b-5p might be an important therapy target in children with acute lung injury.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
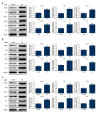
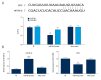
References
-
- Prescott PA. Nursing intensity: Needed today for more than staffing. Nurs Econ. 1991;9(6):409–14. - PubMed
-
- Battie MC, Videman T. Lumbar disc degeneration: Epidemiology and genetics. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(Suppl 2):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Gupta P, Richardson T, Hall M, et al. Effect of inhaled nitric oxide on outcomes in children with acute lung injury: Propensity matched analysis from a linked database. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(10):1901–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

