Mechanism and Regulation of Centriole and Cilium Biogenesis
- PMID: 30601682
- PMCID: PMC6588485
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111153
Mechanism and Regulation of Centriole and Cilium Biogenesis
Abstract
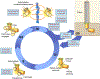
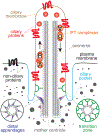
The centriole is an ancient microtubule-based organelle with a conserved nine-fold symmetry. Centrioles form the core of centrosomes, which organize the interphase microtubule cytoskeleton of most animal cells and form the poles of the mitotic spindle. Centrioles can also be modified to form basal bodies, which template the formation of cilia and play central roles in cellular signaling, fluid movement, and locomotion. In this review, we discuss developments in our understanding of the biogenesis of centrioles and cilia and the regulatory controls that govern their structure and number. We also discuss how defects in these processes contribute to a spectrum of human diseases and how new technologies have expanded our understanding of centriole and cilium biology, revealing exciting avenues for future exploration.
Keywords: cell cycle; centriole; centrosome; cilia; ciliopathy; mitosis.
Figures
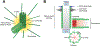
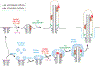

References
-
- Pickett-Heaps JD. 1971. The autonomy of the centriole: fact or fallacy? Cytobios 3: 205–14
-
- Gonczy P 2012. Towards a molecular architecture of centriole assembly. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13: 425–35 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

