Global analysis of N6-methyladenosine functions and its disease association using deep learning and network-based methods
- PMID: 30601803
- PMCID: PMC6331136
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006663
Global analysis of N6-methyladenosine functions and its disease association using deep learning and network-based methods
Abstract
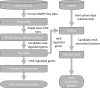
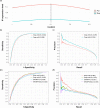
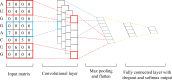
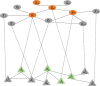
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant methylation, existing in >25% of human mRNAs. Exciting recent discoveries indicate the close involvement of m6A in regulating many different aspects of mRNA metabolism and diseases like cancer. However, our current knowledge about how m6A levels are controlled and whether and how regulation of m6A levels of a specific gene can play a role in cancer and other diseases is mostly elusive. We propose in this paper a computational scheme for predicting m6A-regulated genes and m6A-associated disease, which includes Deep-m6A, the first model for detecting condition-specific m6A sites from MeRIP-Seq data with a single base resolution using deep learning and Hot-m6A, a new network-based pipeline that prioritizes functional significant m6A genes and its associated diseases using the Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) and gene-disease heterogeneous networks. We applied Deep-m6A and this pipeline to 75 MeRIP-seq human samples, which produced a compact set of 709 functionally significant m6A-regulated genes and nine functionally enriched subnetworks. The functional enrichment analysis of these genes and networks reveal that m6A targets key genes of many critical biological processes including transcription, cell organization and transport, and cell proliferation and cancer-related pathways such as Wnt pathway. The m6A-associated disease analysis prioritized five significantly associated diseases including leukemia and renal cell carcinoma. These results demonstrate the power of our proposed computational scheme and provide new leads for understanding m6A regulatory functions and its roles in diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FunDMDeep-m6A: identification and prioritization of functional differential m6A methylation genes.Bioinformatics. 2019 Jul 15;35(14):i90-i98. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz316. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31510685 Free PMC article.
-
DeepM6ASeq: prediction and characterization of m6A-containing sequences using deep learning.BMC Bioinformatics. 2018 Dec 31;19(Suppl 19):524. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2516-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30598068 Free PMC article.
-
m6ATM: a deep learning framework for demystifying the m6A epitranscriptome with Nanopore long-read RNA-seq data.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae529. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae529. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39438075 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine methyltransferases: functions, regulation, and clinical potential.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jul 27;14(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01129-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34315512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine and its role in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Dec 4;18(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1109-9. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31801551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DRUM: Inference of Disease-Associated m6A RNA Methylation Sites From a Multi-Layer Heterogeneous Network.Front Genet. 2019 Apr 3;10:266. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00266. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31001320 Free PMC article.
-
Concepts and methods for transcriptome-wide prediction of chemical messenger RNA modifications with machine learning.Brief Bioinform. 2023 May 19;24(3):bbad163. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad163. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37139545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction of Methyltransferase-like 3-Mediated RNA N6-Methyladenosine Exacerbates the Development of Psoriasis Vulgaris in Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 21;23(20):12672. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012672. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293529 Free PMC article.
-
LITHOPHONE: Improving lncRNA Methylation Site Prediction Using an Ensemble Predictor.Front Genet. 2020 Jun 9;11:545. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00545. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32582286 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of RNA Methylation Status From Gene Expression Data Using Classification and Regression Methods.Evol Bioinform Online. 2020 Jul 20;16:1176934320915707. doi: 10.1177/1176934320915707. eCollection 2020. Evol Bioinform Online. 2020. PMID: 32733123 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

