Purification, characterization and in vitro and in vivo immune enhancement of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves
- PMID: 30601811
- PMCID: PMC6314569
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208611
Purification, characterization and in vitro and in vivo immune enhancement of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves
Abstract
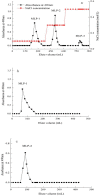
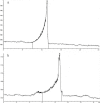
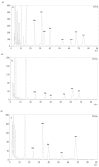
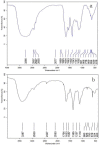
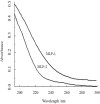
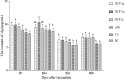
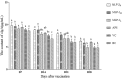
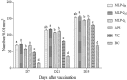
Mulberry leaf polysaccharide (MLP) was extracted and purified by DEAE-52 cellulose and Sephadex G-100 column chromatography to afford two major purified polysaccharides (MLP-1 and MLP-2). The purified polysaccharides were characterized, and their immune-enhancing properties were investigated. MLP-1 had a molecular weight of 9.31×104 Da and was composed of mannose, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, xylose, and arabinose in a molar ratio of 0.71:1.00:2.76:1.13:3.70:2.81. The molecular weight of MLP-2 was 2.22×106 Da, and its monosaccharide constituents were mannose, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, and arabinose in a molar ratio of 1.31:8.45:6.94:1.00:11.96. Infrared spectroscopy showed that each MLP had a typical absorption peak characteristic of sugars, and ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy showed that neither MLP contained nucleic acid or protein components. Then, the abilities of these polysaccharides to stimulate spleen lymphocyte proliferation in mice in vitro were compared by the 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. MLP-2 was more effective than MLP-1; therefore, MLP-2 was chosen for the study of its immune-enhancing effects in vivo. For the in vivo experiments, 14-day-old chickens immunized with Newcastle disease (ND) vaccine were orally administered MLP-2, and Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) was used as the control. Each chicken was orally administered 4 mg or 8 mg of MLP-2 for seven consecutive days starting three days before ND vaccine immunization. MLP-2 significantly improved the ND serum antibody titer and interleukin-2 (IL-2), interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and immunoglobulin A (sIgA) concentrations in tracheal and jejunal wash fluids, and increasing numbers of immune globulin A-positive (IgA+) cells in cecal tonsils and increased body weight. These results indicated that MLP-2 could significantly enhance immune activity and could therefore be utilized as an immunopotentiator drug candidate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mulberry leaf polysaccharide supplementation contributes to enhancing the respiratory mucosal barrier immune response in Newcastle disease virus-vaccinated chicks.Poult Sci. 2021 Feb;100(2):592-602. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.11.039. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 33518112 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from the leaves of maca (Lepidium Meyenii).Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Feb;107(Pt B):2611-2619. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.10.139. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29080819
-
Extraction optimization, characterization and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharides from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves.Carbohydr Polym. 2015 Sep 5;128:52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.04.028. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Carbohydr Polym. 2015. PMID: 26005139
-
Extraction, structural characterization and biological activities of polysaccharides from mulberry leaves: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;257(Pt 2):128669. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128669. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38092124 Review.
-
Extraction, purification, structural modification, activities and application of polysaccharides from different parts of mulberry.Food Funct. 2024 Apr 22;15(8):3939-3958. doi: 10.1039/d3fo05747j. Food Funct. 2024. PMID: 38536669 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential therapeutic target for polysaccharide inhibition of colon cancer progression.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 8;10:1325491. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1325491. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38264044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the structural characterization and pharmacological activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharides.Front Chem. 2025 Mar 14;13:1492533. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1492533. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40161004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Application of Morus and Its Extracts in Animal Production.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;12(24):3541. doi: 10.3390/ani12243541. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production, purification, characterization, and biological properties of Rhodosporidium paludigenum polysaccharide.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 29;16(1):e0246148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246148. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33513164 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Mulberry Leaf Polysaccharide-Caged Liposomes for Effective Oral Drug Delivery in Rat Model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 25;20:5377-5391. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S514455. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40303573 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie QG. Progress in the study of grave epidemic diseases immune prevention and cure of domestic animals and poultry, Chinese Agriculture Science and Technology Press, Beijing, 1999, pp. 143–168.
-
- Fan YP, Hu YL, Wang DY, Guo ZH, Zhao XN, Guo LW, et al. Epimedium polysaccharide and propolis flavone can synergistically stimulate lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and enhance the immune responses to ND vaccine in chickens[J]. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010; 47(2): 87–92. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.05.017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

