Current and Future Distribution of the Lone Star Tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.) (Acari: Ixodidae) in North America
- PMID: 30601855
- PMCID: PMC6314611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209082
Current and Future Distribution of the Lone Star Tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.) (Acari: Ixodidae) in North America
Abstract
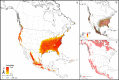
Acarological surveys in areas outside the currently believed leading edge of the distribution of lone star ticks (Amblyomma americanum), coupled with recent reports of their identification in previously uninvaded areas in the public health literature, suggest that this species is more broadly distributed in North America than currently understood. Therefore, we evaluated the potential geographic extent under present and future conditions using ecological niche modeling approach based on museum records available for this species at the Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit (WRBU). The median prediction of a best fitting model indicated that lone star ticks are currently likely to be present in broader regions across the Eastern Seaboard as well as in the Upper Midwest, where this species could be expanding its range. Further northward and westward expansion of these ticks can be expected as a result of ongoing climate change, under both low- and high-emissions scenarios.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Childs JE, Paddock CD. The Ascendancy of Amblyomma americanum as a Vector of Pathogens Affecting Humans in The United States*. Annu Rev Entomol. 2003;48(1):307–37. - PubMed
-
- Mixson TR, Campbell SR, Gill JS, Ginsberg HS, Reichard MV, Schulze TL, et al. Prevalence of Ehrlichia, Borrelia, and Rickettsial agents in Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from nine states. J Med Entomol. 2006;43(6):1261–8. - PubMed
-
- Ostfeld RS, Keesing F. Biodiversity and disease risk: The case of lyme disease. Conserv Biol. 2000;14(3):722–8. 10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.99014.x WOS:000087553900018. - DOI
-
- CDC 2018. Map of established Amblyomma americanum tick populations in the United States 2018. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ticks/maps/lone_star_tick.pdf.
-
- Raghavan RK, Goodin DG, Hanzlicek GA, Zolnerowich G, Dryden MW, Anderson GA, et al. Maximum Entropy-Based Ecological Niche Model and Bio-Climatic Determinants of Lone Star Tick (Amblyomma americanum) Niche. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases. 2016;16(3):205–11. 10.1089/vbz.2015.1837 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

