Common and Differential Transcriptional Actions of Nuclear Receptors Liver X Receptors α and β in Macrophages
- PMID: 30602495
- PMCID: PMC6379585
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00376-18
Common and Differential Transcriptional Actions of Nuclear Receptors Liver X Receptors α and β in Macrophages
Abstract
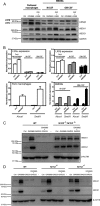
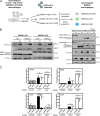
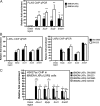
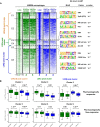
The liver X receptors α and β (LXRα and LXRβ) are oxysterol-activated transcription factors that coordinately regulate gene expression that is important for cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism. In addition to their roles in lipid metabolism, LXRs participate in the transcriptional regulation of macrophage activation and are considered potent regulators of inflammation. LXRs are highly similar, and despite notable exceptions, most of their reported functions are substantially overlapping. However, their individual genomic distribution and transcriptional capacities have not been characterized. Here, we report a macrophage cellular model expressing equivalent levels of tagged LXRs. Analysis of data from chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with deep sequencing revealed that LXRα and LXRβ occupy both overlapping and exclusive genomic regulatory sites of target genes and also control the transcription of a receptor-exclusive set of genes. Analysis of genomic H3K27 acetylation and mRNA transcriptional changes in response to synthetic agonist or antagonist treatments revealed a putative mode of pharmacologically independent regulation of transcription. Integration of microarray and sequencing data enabled the description of three possible mechanisms of LXR transcriptional activation. Together, these results contribute to our understanding of the common and differential genomic actions of LXRs and their impact on biological processes in macrophages.
Keywords: LXR; gene expression; inflammation; liver X receptor; macrophage; nuclear receptor; transcription.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The phospholipid transfer protein gene is a liver X receptor target expressed by macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Mar;23(6):2182-91. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2182-2191.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12612088 Free PMC article.
-
Different roles of liver X receptor alpha and beta in lipid metabolism: effects of an alpha-selective and a dual agonist in mice deficient in each subtype.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Feb 14;71(4):453-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.11.004. Epub 2005 Dec 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16325781
-
Cross-talk between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and liver X receptor (LXR) in nutritional regulation of fatty acid metabolism. II. LXRs suppress lipid degradation gene promoters through inhibition of PPAR signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2003 Jul;17(7):1255-67. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0191. Epub 2003 May 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12730332
-
Liver X receptors in lipid signalling and membrane homeostasis.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018 Aug;14(8):452-463. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0037-x. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29904174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LXR is crucial in lipid metabolism.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005 Jul;73(1):59-63. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2005.04.009. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2005. PMID: 15913974 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation Triggers Liver X Receptor-Dependent Lipogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Jan 3;40(2):e00364-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00364-19. Print 2020 Jan 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31658997 Free PMC article.
-
The LXRB-SREBP1 network regulates lipogenic homeostasis by controlling the synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids in goat mammary epithelial cells.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 7;13(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00774-4. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36336695 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressive Cells Deficient in Liver X Receptor α Protected From Autoimmune Hepatitis.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 26;12:732102. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732102. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34512667 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X receptor alpha ensures blood-brain barrier function by suppressing SNAI2.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Nov 28;14(11):781. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06316-8. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 38016947 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic regulation of macrophage polarization: Where do the nuclear receptors belong?Immunol Rev. 2023 Aug;317(1):152-165. doi: 10.1111/imr.13209. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Immunol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37074820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van de Laar L, Saelens W, De Prijck S, Martens L, Scott CL, Van Isterdael G, Hoffmann E, Beyaert R, Saeys Y, Lambrecht BN, Guilliams M. 2016. Yolk sac macrophages, fetal liver, and adult monocytes can colonize an empty niche and develop into functional tissue-resident macrophages. Immunity 44:755–768. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E, Lin YC, Laslo P, Cheng JX, Murre C, Singh H, Glass CK. 2010. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell 38:576–589. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.05.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
