Hepatoprotective Effect of Baicalein Against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice
- PMID: 30602693
- PMCID: PMC6337302
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24010131
Hepatoprotective Effect of Baicalein Against Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
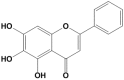
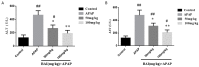
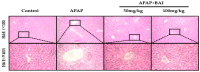
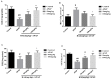
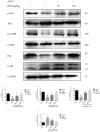
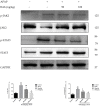
Baicalein (BAI), one of the main components of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, possesses numerous pharmacological properties, including anti-cancer, anti-oxidative, anti-virus and anti-bacterial activities. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the hepatoprotective effect of baicalein against acetaminophen (APAP)-exposed liver injury in mice, and elucidate the underlying hepatoprotective mechanism. Baicalein pretreatment significantly alleviated the elevation of IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α in serum and hepatic in a dose-dependent manner. It also dose-dependently reduced the hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration, as well as the depletion of hepatic superoxide dismutase (SOD), hepatic glutathione (GSH) and hepatic catalase (CAT). Moreover, pretreatment with baicalein significantly ameliorated APAP-exposed liver damage and histological hepatocyte changes. Baicalein also relieved APAP-induced autophagy by regulating AKT/mTOR pathway, LC3B and P62 expression. Furthermore, the hepatoprotective effect of baicalein to APAP-induced liver injury involved in Jak2/Stat3 and MAPK signaling pathway. Taken together, our findings suggested that baicalein exhibits the ability to prevent liver from APAP-induced liver injury and provided an underlying molecular basis for potential applications of baicalein to cure liver injuries.
Keywords: acetaminophen; autophagy; baicalein; inflammation; liver injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Tormentic Acid, a Major Component of Suspension Cultures of Eriobotrya japonica Cells, on Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.Molecules. 2017 May 18;22(5):830. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050830. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28524081 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of chiisanoside against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice.Nat Prod Res. 2019 Sep;33(18):2704-2707. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1460841. Epub 2018 Apr 15. Nat Prod Res. 2019. PMID: 29658369
-
Saponins (Ginsenosides) from the Leaves of Panax quinquefolius Ameliorated Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 May 10;65(18):3684-3692. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b00610. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28429935
-
Protective effects of nicotinamide against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury.Int Immunopharmacol. 2012 Dec;14(4):530-7. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2012.09.013. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23059795 Review.
-
Role and mechanisms of autophagy in acetaminophen-induced liver injury.Liver Int. 2018 Aug;38(8):1363-1374. doi: 10.1111/liv.13866. Epub 2018 May 14. Liver Int. 2018. PMID: 29682868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and ALOX12 and NF-κB Pathways Contribute to the Protective Effect of Baicalein on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 18;10(6):976. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060976. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207230 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Chinese Skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) and Its Extracts for Sustainable Animal Production.Animals (Basel). 2021 Apr 7;11(4):1039. doi: 10.3390/ani11041039. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in Scutellariae radix: A comprehensive review on ethnobotanical uses, processing, phytochemistry, pharmacological effects, quality control and influence factors of biosynthesis.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 20;10(16):e36146. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36146. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39262990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Protective Effect and Mechanism of a Phytochemical Extract from the Wild Vegetable Shutou (Crateva unilocularis Buch.) against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice.Foods. 2023 Aug 18;12(16):3109. doi: 10.3390/foods12163109. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37628108 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese herbs and natural products in hyperuricemia-induced chronic kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 9;13:971032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.971032. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36016570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

