Effective Tetradentate Compound Complexes against Leishmania spp. that Act on Critical Enzymatic Pathways of These Parasites
- PMID: 30602705
- PMCID: PMC6337631
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24010134
Effective Tetradentate Compound Complexes against Leishmania spp. that Act on Critical Enzymatic Pathways of These Parasites
Abstract
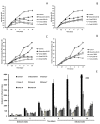
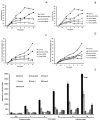
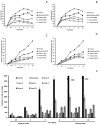
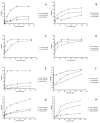
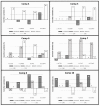
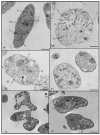
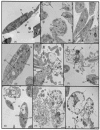
The spectrum and efficacy of available antileishmanial drugs is limited. In the present work we evaluated in vitro the antiproliferative activity of 11 compounds based on tetradentate polyamines compounds against three Leishmania species (L. braziliensis, L. donovani and L. infantum) and the possible mechanism of action. We identified six compounds (3, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 10) effective against all three Leishmania spp both on extracellular and intracellular forms. These six most active leishmanicidal compounds also prevent the infection of host cells. Nevertheless, only compound 7 is targeted against the Leishmania SOD. Meanwhile, on the glucose metabolism the tested compounds have a species-specific effect on Leishmania spp.: L. braziliensis was affected mainly by 10 and 8, L. donovani by 7, and L. infantum by 5 and 3. Finally, the cellular ultrastructure was mainly damaged by 11 in the three Leishmania spp. studied. These identified antileishmania candidates constitute a good alternative treatment and will be further studied.
Keywords: Leishmania spp.; SOD; amastigote; antileishmania; antiproliferative; promastigote; tetradentate polyaminic compounds; ultrastructure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 11 October 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis.
-
- Guerra J.A., Prestes S.R., Silveira H., Coelho L.I., Gama P., Moura A., Amato V., Barbosa M., Ferreira L.C. Mucosal leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis and Leishmania (Viannia) guyanensis in the Brazilian Amazon. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011:5. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000980. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paniz Mondolfi A.E., Stavropoulos C., Gelanew T., Loucas E., Perez Alvarez A.M., Benaim G., Polsky B., Schoenian G., Sordillo E.M. Successful Treatment of Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum with Posaconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55:1774–1776. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01498-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Control of the Leishmaniasis. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2010.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

