Integrin trafficking in cells and tissues
- PMID: 30602723
- PMCID: PMC6597357
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-018-0223-z
Integrin trafficking in cells and tissues
Abstract
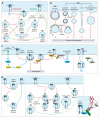
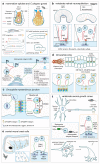
Cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix is fundamental to metazoan multicellularity and is accomplished primarily through the integrin family of cell-surface receptors. Integrins are internalized and enter the endocytic-exocytic pathway before being recycled back to the plasma membrane. The trafficking of this extensive protein family is regulated in multiple context-dependent ways to modulate integrin function in the cell. Here, we discuss recent advances in understanding the mechanisms and cellular roles of integrin endocytic trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial and non-financial competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Maartens AP, Brown NH. Current Topics in Developmental Biology. Vol. 112. Academic Press; Cambridge: 2015. Anchors and Signals: The diverse roles of integrins in development; pp. 233–272. 2015. - PubMed
-
- Mould AP, Humphries MJ. Regulation of integrin function through conformational complexity: Not simply a knee-jerk reaction? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:544–551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

