GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology
- PMID: 30602790
- PMCID: PMC6370056
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0832-5
GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: GABAA receptor signalling mechanisms revealed by structural pharmacology.Nature. 2019 Feb;566(7744):E8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0929-5. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30733619
Abstract
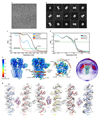
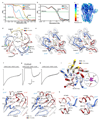
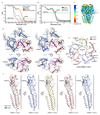
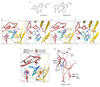
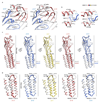
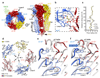
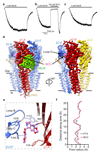
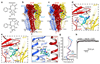
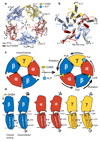
Type-A γ-aminobutyric (GABAA) receptors are ligand-gated chloride channels with a very rich pharmacology. Some of their modulators, including benzodiazepines and general anaesthetics, are among the most successful drugs in clinical use and are common substances of abuse. Without reliable structural data, the mechanistic basis for the pharmacological modulation of GABAA receptors remains largely unknown. Here we report several high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures in which the full-length human α1β3γ2L GABAA receptor in lipid nanodiscs is bound to the channel-blocker picrotoxin, the competitive antagonist bicuculline, the agonist GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid), and the classical benzodiazepines alprazolam and diazepam. We describe the binding modes and mechanistic effects of these ligands, the closed and desensitized states of the GABAA receptor gating cycle, and the basis for allosteric coupling between the extracellular, agonist-binding region and the transmembrane, pore-forming region. This work provides a structural framework in which to integrate previous physiology and pharmacology research and a rational basis for the development of GABAA receptor modulators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

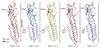


Comment in
-
An in-depth structural view of a GABAA brain receptor.Nature. 2019 Jan;565(7740):436-438. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-07843-7. Nature. 2019. PMID: 30666053 No abstract available.
-
Cryo-electron microscopy reveals informative details of GABAA receptor structural pharmacology: implications for drug discovery.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Jul;7(Suppl 3):S144. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.06.23. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31576351 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sieghart W. Structure and pharmacology of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor subtypes. Pharmacol Rev. 1995;47:181–234. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:291–313. - PubMed
-
- Möhler H. GABAA receptors in central nervous system disease: anxiety, epilepsy and insomnia. J Recept Signal Transduct. 2006;26:731–740. - PubMed
-
- Olsen RW. Analysis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type A receptor subtypes using isosteric and allosteric ligands. Neurochem Res. 2014;39:1924–1941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

