Diagnostic utility of, and influence of tobacco usage and genetic predisposition on, immunoglobulin A, rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated peptide auto-antibodies in South African rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 30602956
- PMCID: PMC6306983
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v18i2.14
Diagnostic utility of, and influence of tobacco usage and genetic predisposition on, immunoglobulin A, rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated peptide auto-antibodies in South African rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
Background: The immunoglobulin A isotypes of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) are associated with disease severity and progression in Caucasian rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, as well as with genetic predisposition and tobacco use.
Objectives: To compare levels of ACPA-IgA and RF-IgA with those of ACPA-IgG and cRF in a cohort of black South African RA patients and healthy controls.To investigate the relationship between IGA autoantibodies and disease severity, genetic predisposition and tobacco use.
Methods: RF-IgA and ACPA-IgA were determined in a cohort of predominantly black South African RA patients (n=75) in relation to serodiagnostic and prognostic potential, as well as tobacco use and genetic predisposition. Healthy control subjects were included to determine sensitivity, specificity and predictive values.ACPA-IgG/IgA and RF-IgA were determined by enzyme immunoassay and hs-CRP and cRF by nephelometry. Cotinine levels were determined by ELISA.
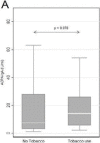
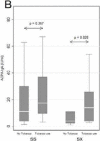
Results: The frequencies of ACPA-IgA and RF-IgA were 31% and 88% respectively compared to 88% for both types of traditional autoantibody procedures. ACPA-IgA was significantly higher (p=0.007) in patients with short disease duration, while linear regression analysis revealed a positive relationship with baseline disease activity scores. Levels of ACPA-IgG and ACPA-IgA were significantly higher in tobacco users who carried the HLA shared epitope.
Conclusion: Although lacking in serodiagnostic superiority over cRF and ACPA-IgG, inclusion of RF-IgA and ACPA-IgA in autoantibody panels may provide insights into disease pathogenesis, interactions between tobacco usage and HLA genotype in the production of potentially disease-triggering ACPA-IgA antibodies.
Keywords: South Africa; Tobacco usage; anti-citrullinated peptide; genetic predisposition; immunoglobulin A; rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Smoking as a risk factor for rheumatoid arthritis: predominant association with IgA autoantibodies - comprehensive analysis of anti-modified protein antibodies with smoking and genetic risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 May 8;27(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03543-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40340864 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Autoantibody Isotypes Increases the Sensitivity of Serodiagnostics in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 24;9:876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00876. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29740454 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of IgA anti-citrullinated protein antibodies and rheumatoid factor in an early arthritis population with a treat-to-target approach.Immunol Res. 2024 Oct;72(5):982-990. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09500-w. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38960995 Free PMC article.
-
Determining in which pre-arthritis stage HLA-shared epitope alleles and smoking exert their effect on the development of rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 Jan;81(1):48-55. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220546. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022. PMID: 34285049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical presentation and treatment response in ACPA-negative rheumatoid arthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2025 Mar;92(2):105823. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2024.105823. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Joint Bone Spine. 2025. PMID: 39577740 Review.
Cited by
-
Sexuality and other issues in Africa and beyond.Afr Health Sci. 2018 Jun;18(2):i-iii. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v18i2.1. Afr Health Sci. 2018. PMID: 30602976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, 3rd, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569–2581. - PubMed
-
- Hu ZD, Deng AM. Auto-antibodies in pre-clinical autoimmune disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;437:14–18. - PubMed
-
- Meyer PW, Ally MM, Anderson R. Reliable and cost-effective serodiagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2016;36(6):751–758. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
