Simulation of an optimized technique based on DS-CDMA for simultaneous transmission of multichannel biosignals
- PMID: 30603162
- PMCID: PMC6208472
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-017-0018-3
Simulation of an optimized technique based on DS-CDMA for simultaneous transmission of multichannel biosignals
Abstract
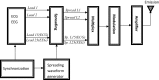
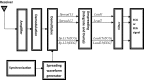
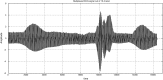
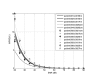
Telemedicine is becoming increasingly, with applications in many areas of healthcare, such as home telecare of the elderly, diagnosis at a distance and robotic surgery. The simultaneous transmission of several leads of biomedical signals should be considered in telemedicine, given the many benefits it brings. Code division multiple access (CDMA) is a multiple access technique that enables users to transmit independent information simultaneously within the same bandwidth. The direct sequence CDMA (DS-CDMA) is a variant of the CDMA technique in which a pseudorandom sequence having a higher bandwidth than the information signal is used to modulate the information signal directly. Biomedical signals are confidential; thus, their transmission must be secured. In this paper we propose a protocol similar to DS-CDMA for the simultaneous transmission of all of the leads of some multichannel biomedical signals. We assigned orthogonal codes to different leads of a signal. The convolution of each lead with the code gives a signal spread over a broad frequency band. All of the spread signals are then mixed to produce a single composite signal. This composite signal is frequency modulated, amplified and transmitted. At the reception, inverse functions to the previous are developed to perform demodulation, demultiplexing and extraction of the physiological signals transmitted. We used the discrete Walsh functions as codes. The results obtained are satisfactory, even in situations where the noise disturbances are significant.
Keywords: Biomedical multichannel signals; CDMA transmission; ECG; EEG; Telemedicine; Walsh functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThere is no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wang C, Lu W, Narayanan MR, Redmond SJ, Lovell NH. Low-power technologies for wearable telecare and telehealth systems: a review. Biomed Eng Lett. 2015;5(5):1–9. doi: 10.1007/s13534-015-0174-2. - DOI
-
- Tchiotsop D, Kanaa T, Fogue M, Tchouani Njomo AF, Kentsa Zana K. Low cost and low power ECG recorder suitable for low incomes populations. Int J Electron Commun Comput Eng. 2015;6(4):558–564.
-
- Nasrabadi AM, Heidari Kani M. Design of ECG acquisition and transmission via Bluetooth with heart disease and diagnosis. In: Proceedings of IEEE international workshop on medical measurements and application; 2011. p. 55–58.
-
- Silapaporn P, Chutatape O. Continous ECG Transmission via mobile Telephone Network and waiting time of packets for smooth display. In: Proceedings of IEEE computational intelligence, communication systems and network; 2012. p. 137–142.
-
- Wang IJ, Liao LD, Wang YT, Chen CY, Lin BS, Lu SW, Lin CT. A wearable mobile electrocardiogram measurement device with novel dry polymer based electrodes. In: Proceedings of IEEE region 10 conference, Tencon; 2010. p. 379–384.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
