Real-time biofeedback device for gait rehabilitation of post-stroke patients
- PMID: 30603178
- PMCID: PMC6208514
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-017-0036-1
Real-time biofeedback device for gait rehabilitation of post-stroke patients
Abstract
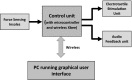
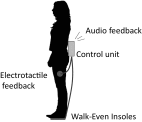
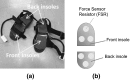
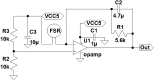
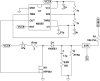
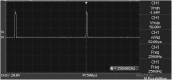
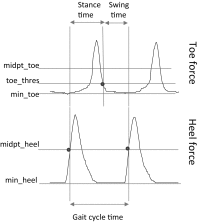
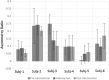
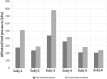
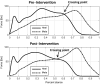
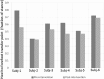
In this work, we develop a device, called 'Walk-Even', that can provide real-time feedback to correct gait asymmetry commonly exhibited in post-stroke survivors and persons with certain neurological disorders. The device computes gait parameters, including gait time, swing time, and stance time of each leg, to detect gait asymmetry and provide corresponding real-time biofeedback by means of auditory and electrotactile stimulation to actively correct the user's gait. The system consists of customized force-sensor-embedded insoles adjustable to fit any shoe size, electrotactile and auditory feedback circuits, microcontroller, and wireless XBee transceivers. The device also offers data saving capability. To validate its accuracy and reliability, we compared the gait measurements from our device with a commercial gait and balance assessment device, Zeno Walkway. The results show good correlation and agreement in a validity study with six healthy subjects and reliability study with seventeen healthy subjects. In addition, preliminary testing on six post-stroke patients after an 8-week training shows that the Walk-Even device helps to improve gait symmetry, foot pressure and forefoot loading of the affected side. Thus, initial testing indicates that the device is accurate in measuring the gait parameters and effective in improving gait symmetry using real-time feedback. The device is portable and low cost and has the potential for use in a non-clinical setting for patients that can walk independently without assistance. A more extensive testing with stroke patients is still ongoing.
Keywords: Biofeedback; Gait asymmetry; Rehabilitation; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors (I-Hung Khoo, Panadda Marayong, Vennila Krishnan, Michael Balagtas, Omar Rojas, Katherine Leyba) declare that they have no conflict of interests in relation to the work in this article.Approval was obtained from the CSULB Institutional Review Board for the experiment involving human subjects.
Figures


References
-
- Kim SY, Yang L, Park IJ, Kim EJ, Park MS, You SH, Kim YH, Ko HY, Shin YI. Correction to “Effects of Innovative WALKBOT Robotic-Assisted Locomotor Training on Balance and Gait Recovery in Hemiparetic Stroke: a Prospective, Randomized, Experimenter Blinded Case Control Study With a Four-Week Follow-Up”. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2015;23:1128. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2015.2497058. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
